What is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the way you’ve configured certain parts of your website so that it can be indexed for the web. It covers all of the nitty-gritty, behind-the-scenes aspects, such as crawling, indexing, site structure, migrations, page speeds, core web vitals, and more.
If you’re at all concerned with how your site is ranking (and if you’re here, you probably are) it’s something that simply can’t be overlooked. Technical SEO plays a pivotal role in shaping your website’s online visibility and search engine rankings.
How Does Technical SEO Work?
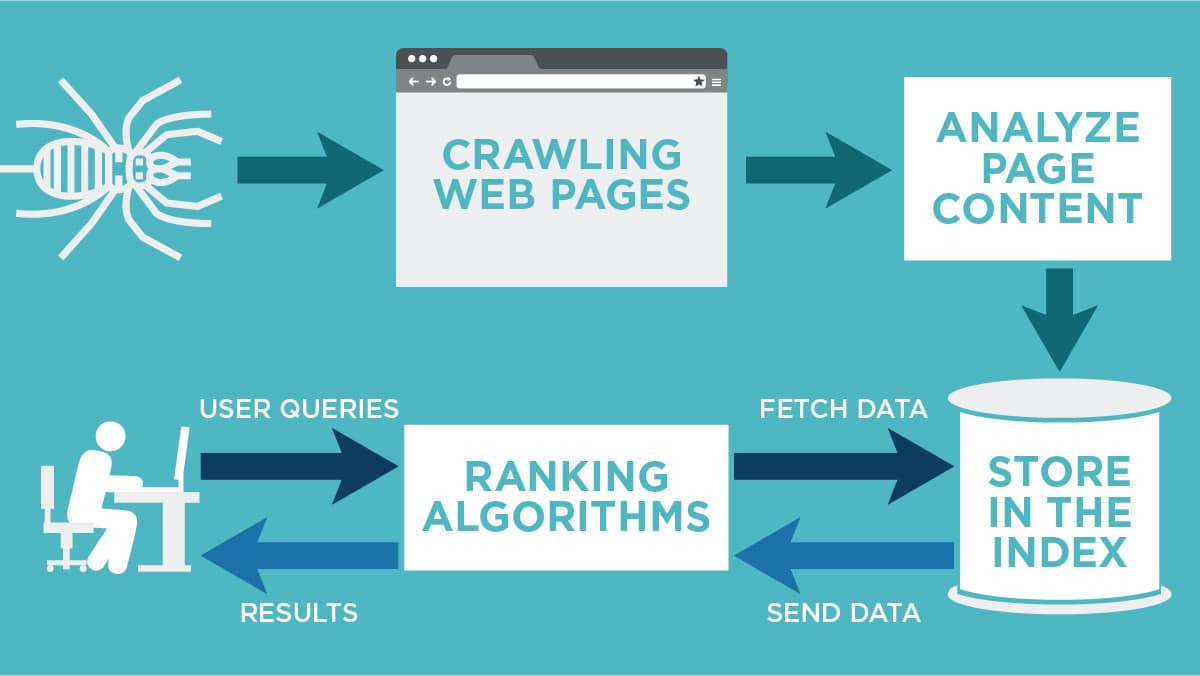
Understanding the mechanics that shape how search engines perceive and rank your website is pivotal for online success. Let’s explore two core components—indexing and crawling.
Process of Indexing and Crawling the Web
Indexing
Consider indexing the bedrock of technical SEO. It’s the gatekeeper that determines whether your web pages find their place within search engine databases.
As search engines meticulously scan your site during the crawling process, they extract vital information, categorize it, and store it for future retrieval. This organized database becomes the foundation of search results, highlighting the profound impact of effective indexing practices.
Crawling
Now, picture crawling as indexing’s counterpart. This process involves search engine bots meticulously traversing your website’s interconnected pages.
By carefully following links, these bots uncover every layer of your content, structural layout, and technical nuances. The art of crawling is key to ensuring comprehensive website coverage.
To achieve this, strategic measures come into play—streamlined sitemaps, coherent URL structures, and astute management of internal linking all play their roles in facilitating efficient crawling.
Why is Technical SEO Important?
Let’s say your content is top-notch, but your technical SEO is not up to standard. Your site won’t end up ranking. This is because creating great content doesn’t really matter if nobody can find or see it.
Although search engines are getting better at crawling, indexing, and understanding intent, they’re still far from perfect. Therefore, good website content needs to be complemented by a strong technical SEO foundation.
If your site is improperly indexed, Google, Bing, Facebook, and other search engines won’t know when to show your site on search result pages.
Performing a technical SEO audit on your website will ensure that you have the proper framework in place so that all of the hard work you’ve done on your site will be indexed and ranked!
Let’s talk about the most common technical SEO mistakes and what you can do to fix them.
Common SEO Mistakes
Mistake #1: Duplicate Content
If there’s one thing Google loves, it’s unique content.
That means that duplicate content is a huge problem if you’re trying to rank on the first page of the search results.
Use tools such as Screaming Frog, Deep Crawl, or SEMRush to find out if you have a duplicate content issue. These tools will crawl your site, as well as other sites on the internet, to find out if your content has been re-posted anywhere.
This could happen when someone else re-posts your content on a different URL or if you have the same content posted on a page and on a post.
To combat this problem, make sure every page is unique. Every page should have its own URL, title, description, and H1/H2 headings. Your H1 heading should be a visible headline that contains your primary keyword. Be sure to put a direct keyword in every section of your page to capitalize on the strength of your keywords.
You should even be careful when you reuse images and the alt-tags that accompany those images. While these tags should contain keywords, they can not be identical. Come up with ways to incorporate the keywords while being different enough that your tags don’t get indexed as duplicate content.
Also, look for duplicate content in your structured data or schema. This is often an overlooked website aspect that can negatively impact your ranking. Google has a great Schema Markup tool that will help you make sure that duplicate content is not appearing in your schema.
Duplicate Content
Mistake #2: Rel=canonical Issues
You can use rel=canonicial to help associate a page with another page. This helps to boost credibility and limit duplicate content without hurting your ranking.
It tells search engines that the page with rel=canonical is the one that should be indexed.
However, if used in the wrong place, it could cause some confusion and lead search engines to not rank your page at all.
Go through the code on all of your pages to locate rel=canonical and make sure it’s being utilized properly.
Mistake #3: Title Tag Issues
Title tags can have a variety of issues that affect SEO, including:
- Duplicate tags
- Missing title tags
- Too long or too short title tags
Your title tags, or page titles, help both users and search engines determine what your page is about, making them an (understandably) important part of the optimization process.
Crafting effective title tags involves a strategic approach. To get your title tags just right, you need to start with the basics:
- Conciseness—Your title tag should be 50-70 characters long. To avoid technical issues, make sure you don’t have any duplicates on your site.
- Keywords—Employ relevant keywords to aid Google’s comprehension and potential ranking. Avoid overstuffing.
- Descriptiveness—Create informative titles that mirror your content, enticing clicks.
- Modifiers—Enhance with words like “Best,” “Top,” “Guide” for context and visibility.
- Uniqueness—Craft distinct titles for each webpage, preventing confusion and boosting search visibility. These steps enhance your title tags, elevating your page’s relevance and discoverability in search results.
Outside of the technical realm, a solid, click-worthy title will include:
- Dates
- Numbers
- Capitalization
- Emotion
Example of a Title Tag
Mistake #4: H1 Tag Issues
Header (H1) tags are another important component of on-page SEO.
While title tags appear in search results, H1 tags are visible to users on your page. The two should be different.
While it’s not recommended to have more than one H1 tag per page, many are commonly missing altogether or are duplicated in the title tag.
Big no when it comes to SEO. Always make sure you include one unique H1 per page.
To make the most of your H1 tag, make sure that it includes the keyword you’re targeting on the page, accurately reflects the page’s content, and is between 50-60 characters long.
Mistake #5: Not Using Meta Descriptions
A page’s meta description is a short snippet that summarizes what your page is about.
Search engines generally display them when the searched-for phrase appears in the description, which is why it’s so important to optimize the meta description for SEO.
Oftentimes, sites that don’t utilize their meta descriptions (or duplicate them) will find their SEO suffering for it.
For best results, always include a meta description (if you use WordPress, this will be found at the bottom of the posting page), aim for 120 – 160 characters and make sure any important keywords are included before the possible cut-off.

Meta Titles & Descriptions
Mistake #6: You’re Using Meta Refresh
Meta refresh is an (outdated) way of redirecting users to another page.
These days, most opt for 301 redirects. Google does not recommend using the meta refresh and notes that it will not have the same benefits as a 301.
Moz has this to say about them: “They are usually slower, and not a recommended SEO technique. They are most commonly associated with a five-second countdown with the text “If you are not redirected in five seconds, click here.” Meta refreshes do pass some link juice, but are not recommended as an SEO tactic due to poor usability and the loss of link juice passed.”
Mistake #7: Low Word Count
While simplicity has its merits, underestimating text length can harm SEO efforts.
Previously, debates swirled around word count’s SEO impact. Although not a direct ranking factor, word count aids in conveying comprehensive information.
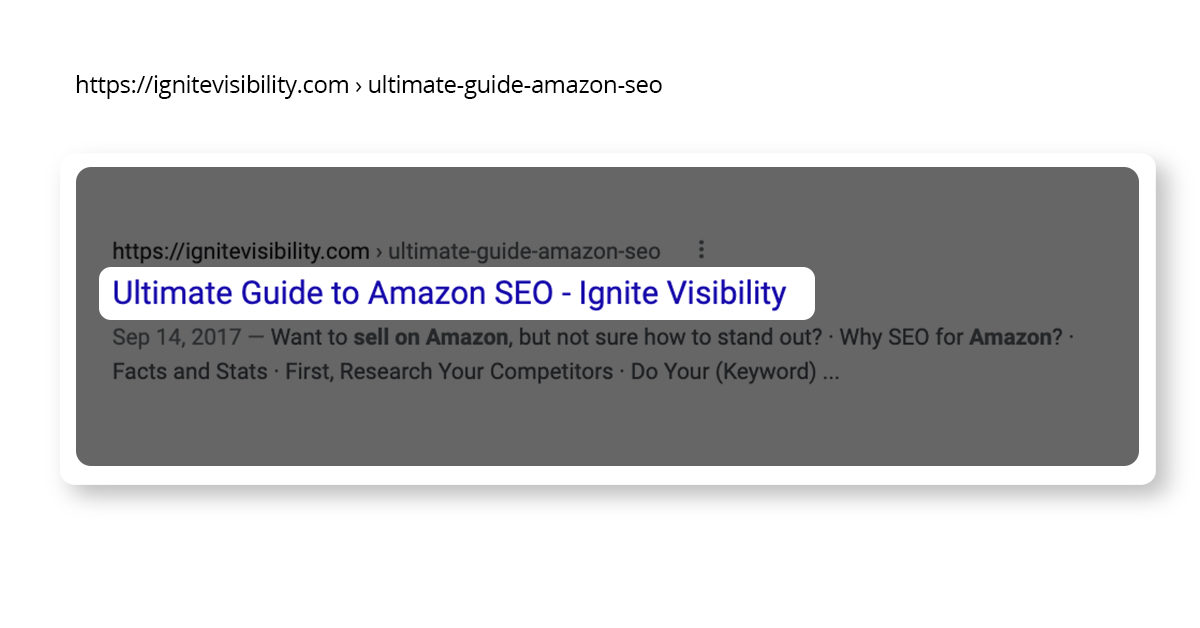
In today’s SEO landscape, longer content typically performs better as it aids search engines in understanding user intent. Aim for at least 300 for regular posts and 900 words for cornerstone content. Product pages can manage 200 words. However, the sweet spot for blog length appears to be between 1,760 and 2,400 words, with posts over 1,000 words consistently delivering stronger results.
As algorithms advance, comprehensive content remains pivotal for value and visibility.
Mistake #8: Hidden Text
Unnecessarily lengthy pages can slow down site speed (they need to be really big though).
Things like terms & conditions or location info can be meant for a single page, but end up embedded in all site pages.
Make sure to scan your site using a tool like Screaming Frog to make sure the word count is what you expect and there’s no hidden text.
Mistake #9: Incorrect Language Declaration
Ideally, you want your content delivered to the right audience – which also means those that speak your language.
In fact, a site’s language declaration is an often overlooked aspect of technical SEO.
Be sure to declare your default language so that Google is always able to translate your page as well as know your location. Your location can affect your international SEO, as well as your technical SEO.
To check whether you’ve done this properly, use this list when verifying your language and country inside of your site’s source code.
Mistake #10: Missing Alt Text Tags
Alt-text is great for two reasons.
One, they make your site more accessible. People who visit your site who are visually impaired can use these tags to know what the images on your site are and why they are there.
Second, they are good from a technical SEO standpoint, too, since they provide more space for text content that you can use to help your site get ranked.
Example of Alt Text for Images
Mistake #11: Broken Images
A good rule of thumb is to always link an image. Whether the link leads to another website or a different page on your own site, be sure to send the user somewhere when they click on each of your images.
Images that lead to nowhere are a surefire way to increase your bounce rate, which will then affect your technical SEO.
Even if you are adding links to all of your images, you’ll want to check them periodically to make sure that site errors or domain changes haven’t negatively affected your links.
Broken images are common and often occur due to site or domain changes or a change in the file after publishing.
If you come across any of these on your site, make sure you troubleshoot fast.
Mistake #12: Poor Internal Linking Structure
Internal linking ranks high in effective SEO strategies. And if you’re not strategizing properly, it could cause some major SEO problems.
To make sure yours is as effective as possible, make sure your pages connect to each other through practical navigational links with optimized anchor text.
Internal Linking for SEO
Mistake #13: Broken Internal Links on Your Website
When crawling your website for indexing purposes, Google depends on the internal links within your page. If these links are broken, it won’t know where to go next.
Broken internal links also tank your credibility. Why would users want to use your website if it’s full of 404 error messages?
To find broken links, use a tool like Screaming Frog. With this tool’s help, you can enter your URL and it will produce any broken links or 404 errors. Once you know where they exist, you can repair or remove them.
Mistake #14: Broken External Links on Your Website
Much like internal links, you don’t want links intending to lead to your site to lead to an error message instead.
A lack of working backlinks will reduce the number of pages that appear in search engines.
Just as you would for internal links, you can use an SEO tool like Screaming Frog to scan your site for external broken links.
Unfortunately, fixing broken backlinks isn’t quite as easy. Because these are hosted on outside sites, your first line of defense should be to contact the site the link came from and ask them to remove it.
Mistake #15: Questionable Link-Building Practices
While link building itself gives an obvious boost in search rinks, doing so in a questionable manner could result in penalties.
Beware of “black hat” strategies like link exchanges. Yes, they’ll get you a lot of links fast, but they’ll be low quality and won’t improve your rankings.
Other questionable “link scheme” behavior that you should avoid includes:
- Buying or selling links
- Automated programs or services
Mistake #16: Incorrect Use of 301 & 302 Redirects
Know the difference between a 301 redirect and a 302 redirect and when to use each of them.
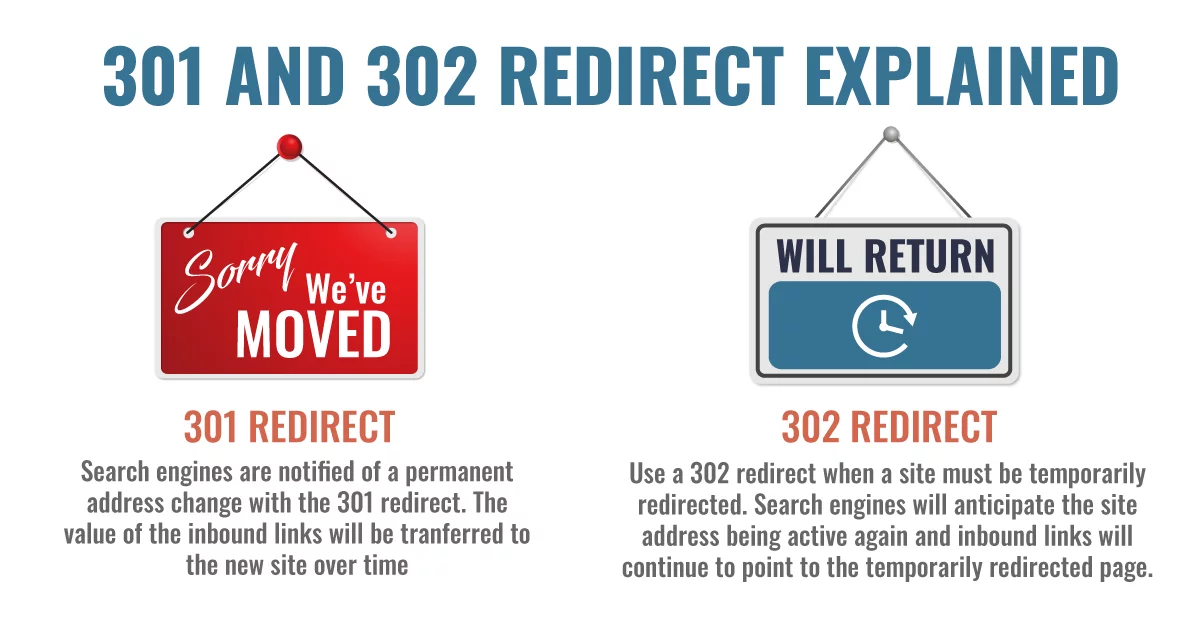
301 Redirects vs 302 Redirects
A 301 redirect is permanent. Use this when you are planning to permanently replace or redirect a page to another location. This type of redirect will let the search engines know that they can stop crawling or indexing this page.
A 302 redirect is a temporary redirect. This code lets the indexers know that this page is currently undergoing some changes but that it will be back online soon. It lets them know that they should continue to crawl or index this page.
If you’re planning to permanently replace or redirect a page, use the correct redirect so search engines don’t continue to crawl or index a page you’re no longer using.
Mistake #17: You’re Not Using Using Custom 404 Pages
Someone might link to your site with an invalid URL. It happens to the best of us, and unfortunately, causes SEO problems in the process.
When that does happen, don’t show the visitor a generic 404 error message with a white background.
Instead, deliver a user-friendly 404 error message. Consider your audience. If they’re tech-savvy, keep 404 explanations concise. For others, explain the error in a friendly manner.
Graphics are great but include essential info in copy or alt-text. Provide homepage links, a search bar, and a clear CTA. You can also provide a link to your home page so users can search for the article or page they were hoping to access.
Mistake #18: Using Soft 404 Errors
When a search engine sees a 404 redirect, it knows to stop crawling and indexing that specific page.
However, if you use soft 404 errors, a code 200 is returned to the indexer. This code tells the search engine that this page is working as it should. Since it thinks that the page is working correctly, it will continue to index it.
Mistake #19: There are Too Many Nofollow Links
Formerly, Google treated Nofollow links as commands, refraining from crawling or indexing them. Now, Google considers Nofollow as a hint. These links, marked with a rel=”nofollow” HTML tag, instruct search engines to disregard them and not pass PageRank, potentially not affecting rankings.
Common scenarios for Nofollow links include:
- Not endorsing a linked page (use rel=”nofollow”).
- Sponsored or paid links (use rel=”sponsored”).
- Affiliate links (use rel=”sponsored”).
- User-generated content (use rel=”ugc”).

Mistake #20: There are Too Many Nofollow Exit Links
The nofollow attribute was once misused for PageRank sculpting, but this practice is obsolete due to Google’s changes.
Despite this, some misconceptions linger.
Two incorrect uses of nofollow include applying it to all external links (ineffective and possibly detrimental) and using it on internal links (inferior to other methods like robots meta tags for controlling crawling and indexing).
Mistake #21: Upper Case vs. Lower Case URLs
SEO problems come in all shapes and sizes, or in this instance, cases.
This has become less of a problem of late, but still comes up for those using .net.
Mainly, servers won’t always redirect sites using uppercase to the lowercase URL.
If this is happening to you, use this rewrite module to fix the problem.
Mistake #22: Messy URLs on Webpages
When URLs are automatically generated, search engine friendliness isn’t necessarily taken into consideration.
This is why you’ll end up with messy, unintelligible URLs like “index.php?p=367595.”
It’s not pretty, and it’s not SEO-friendly.
Try cleaning them up and adding relevant keywords to your URLs.
Mistake #23: Your Server Header Has the Wrong Code
While you’re performing your technical SEO audit, be sure to check your Server Header. There are multiple tools on the internet that will serve as a Server Header Checker.
These tools will tell you what status code is being returned for your website. Pages with a 4xx or 5xx status code are marked as problem sites and search engines will shy away from indexing them.
If you find out that your server header is returning a problem code, you’ll want to go into the backend of your site and fix it so that your URL status code is a positive one.
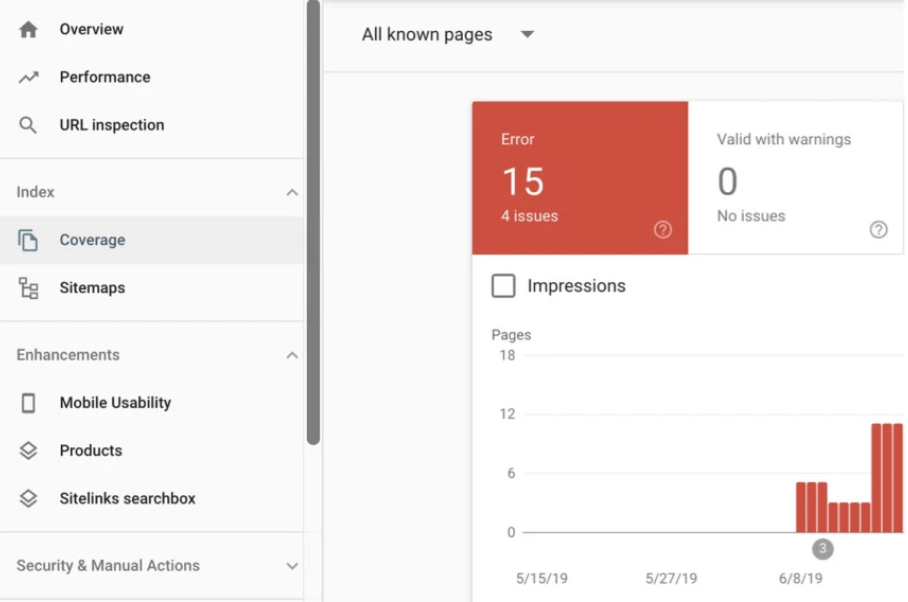
Use Google Search Console to Find 5xx Errors
Mistake #24: Low Text to HTML Ratio
Indexers like content that loads quickly and easily!
Text and copy make it easier for indexers to know what your site is about and which keywords it relates to. If you make it too confusing, the search engines won’t try to figure it out. They just won’t index the pages that confused them.
If you have too much backend code on your site, it causes it to load too slowly. Make sure that your text outweighs your HTML code.
This problem has an easy solution — either remove unnecessary code or add more on-page text content. You can also remove or block any old or unnecessary pages.
Mistake #25: There are Query Parameters at the End of URLs
Familiar with the overly-long URL?
This often happens when certain filters are added to URLs such as color, size, etc. Most commonly it affects ecommerce sites.
I’ve had this issue with a lot of sites… Many times the parameters cause duplicate content as well.
The biggest issue here? It uses up your crawl budget, so make sure you take the time needed to clean up your URLs.
Mistake #26: Improper Move to New Website or URL Structure
Updating and moving websites is an important part of keeping a business fresh and relevant, but if the transition isn’t managed properly, there’s a lot that could go wrong.
Mainly, a loss in traffic.
It’s important to keep track of all URLs and ensure there are no duplicates and that 301 redirects are directed properly.
For more on how to migrate your site and maintain your traffic, check out the full guide here.
Mistake #27: Your Sitemap is Outdated, Broken or Missing
Sitemaps are really important as they are delivered to both Google and Bing Webmasters to assist them with indexing your site.
They are super easy to make — in fact, most web design or hosting sites will prepare one for you. But this is also an aspect where your technical SEO can fail.
Much like your internal links, site index crawlers use your sitemap to determine which page to go to next. If this map is outdated, missing, or broken, they won’t know where to go.
If they don’t know how to crawl your content, they won’t know how to index it. If they can’t index your site, it can’t be ranked.
Make sure your sitemap is up-to-date and contains any changes you have made to your site’s pages.
If you’re struggling with creating a sitemap, a plug-in like Yoast can make one for you.
Site Map Organization Example
Mistake #28: Too Many Plugins
While plugins can enhance functionality and design, an excess of them can bloat your website and slow down its performance.
Each plugin adds code and potential compatibility issues, impacting page load times and user experience. Regularly review and streamline your plugin usage.
Remove those that are redundant or unnecessary, and opt for well-coded, lightweight alternatives whenever possible.
Prioritizing quality over quantity when it comes to plugins ensures your website remains fast, responsive, and easy to navigate, contributing positively to both user satisfaction and SEO rankings.
Mistake #29: Ignoring Schema Markup
In the quest for better search visibility, don’t overlook the power of schema markup.
Schema markup is code that you add to your website to provide search engines with detailed information about your content. This can result in rich snippets—a visually enhanced presentation of search results—that draw users’ attention and increase click-through rates.
Ignoring schema markup means missing out on a chance to stand out in the search results, particularly when it comes to product details, reviews, events, and other structured content.
Incorporating schema markup might require technical finesse, but the potential for improved search performance and user engagement is well worth the effort.
Mistake #30: A Robots.txt File Error
This is a big hit to your technical SEO.
This is a big one to pay attention to when running down your technical SEO checklist.
Something as seemingly insignificant as a misplaced letter in your robots.txt file can do major damage and cause your page to be incorrectly indexed.
Be careful when ordering your file (or make sure your developer is); you could have the correct commands listed, but if they don’t work together correctly it could lead to unintended URLs being crawled.
A misplaced “disallow” is another thing to be on the lookout for. This will signal Google and other search engines to not crawl the page containing the disallow, which would keep it from being properly indexed.
You can test the health of your robots.txt file by using the test tool inside of the Google Search Console.
A misplaced “disallow” is another thing to be on the lookout for. This will signal Google and other search engines to not crawl the page containing the disallow, which would keep it from being properly indexed.
Mistake #31: Your Core Web Vitals Aren’t Good
Core Web Vitals are a fairly new aspect when it comes to technical SEO but don’t overlook it.
This Google tool will tell you essentially how your website is performing. It checks whether it loads quickly, is user-friendly, and is safe.
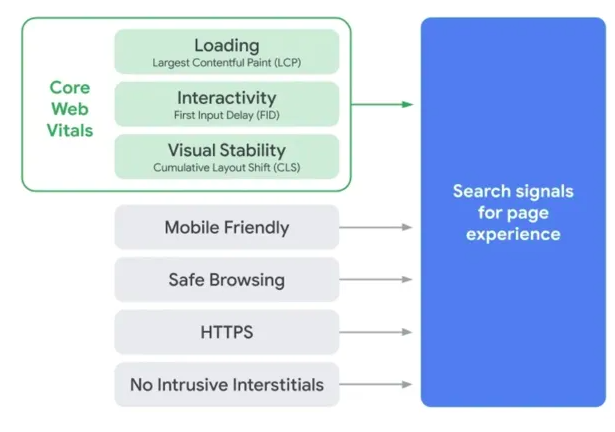
Core Web Vitals
You’ll want Google to approve of your core web vitals so it will give your site a high ranking. If Google feels as if it cannot trust your site, it will not recommend it to its users.
Mistake #32: Your Website Has a Slow Load Time
If your website is loading slowly, it’s likely not ranking well, which can undoubtedly cause some major SEO issues.
Google itself has said:
“Like us, our users place a lot of value in speed — that’s why we’ve decided to take site speed into account in our search rankings. We use a variety of sources to determine the speed of a site relative to other sites.”
Luckily, site speed can be monitored and any issues should be dealt with as soon as possible.
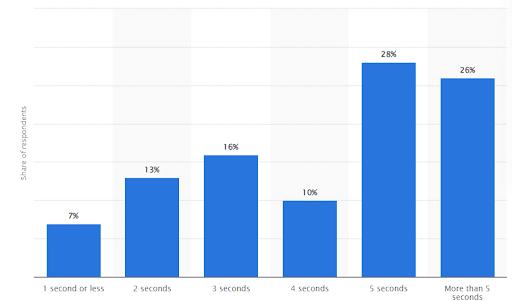
Google hasn’t set official page load time guidelines, but experts agree that 2 seconds or less is ideal. According to a recent Statista survey, around 16% of users said they will wait up to 3 seconds, and just 26% are patient enough to endure over 5 seconds.
Some ways to increase site speed include:
- Enabling compression – You’ll have to talk to your web development team about this. It’s not something you should attempt on your own as it usually involves updating your web server configuration. However, it will improve your site speed.
- Optimizing images – Many sites have images that are 500k or more in size. Some of those pics could be optimized so that they’re much smaller without sacrificing image quality. When your site has fewer bytes to load, it will render the page faster.
- Leveraging browser caching – If you’re using WordPress, you can grab a plugin that will enable you to use browser caching. That helps users who revisit your site because they’ll load resources (like images) from their hard drive instead of over the network.
- Using a CDN – A content delivery network (CDN) will deliver content quickly to your visitors by loading it from a node that’s close to their location. The downside is the cost. CDNs can be expensive. But if you’re concerned about user experience, they might be worth it.
Mistake #33: Poor Mobile Experience
These days, this one’s a no-brainer.
In 2016, Google announced its intention to start mobile-first indexing:
“To make our results more useful, we’ve begun experiments to make our index mobile-first. Although our search index will continue to be a single index of websites and apps, our algorithms will eventually primarily use the mobile version of a site’s content to rank pages from that site, to understand structured data, and to show snippets from those pages in our results.”
Mobile Experience
To properly optimize for mobile, you must take everything from site design and structure of your page to page speed into consideration.
Mistake #34: Your Website Has Poor Navigation
If users can’t easily navigate your site, they’re unlikely to engage and will prove less useful to visitors.
In turn, that could lead search engines to consider your site to have low authority, which will adversely affect your rankings.
Mistake #35: Still Using HTTP
Since web security is always on everyone’s minds, all indexed sites now use HTTPS.
An announcement from Google stated that they would soon start marking any non-HTTPS sites as non-secure if they require credit cards or passwords.
Search engines don’t want to harm their own credibility by sending their users to non-secure sites. If your website is not secure, they just won’t index it.
Using an HTTP site is a fatal mistake when it comes to your technical SEO.
Mistake #36: You’re Not Using Local Search and Structured Data Markup
Local searches drive a lot of search engine queries, and Google certainly recognizes that.
This is why a presence on search data providers like Yelp, Facebook, etc. is essential. Make sure your contact information is consistent on all pages.
Mistake #37: Multiple Versions of Homepage
We’ve discussed previously that duplicate content presents a problem but that problem grows even bigger when it’s your homepage that’s duplicated.
You’ll want to make sure that you don’t have multiple versions (www and non-www, .index.html versions, etc.) of your homepage.
You can find out if this is happening with your site by simply Googling Site: [insert version of the site you’re looking for]. The results that come back will tell you if those versions are live or indexed.
If you do find out that multiple versions of your site are live, add a 301 redirect to the duplicate page to point search engines and users in the direction of the correct homepage.
Mistake #38: You’re Not Using Breadcrumb Menus
Put breadcrumb links on your web pages. That’s an especially great idea if you’re running an ecommerce site with lots of categories and subcategories.
You’ve probably seen breadcrumbs as you’ve wandered about cyberspace. They look like this:
Categories > Electronics > Mobile Devices > Smartphones
Each one of those words or phrases is a link. That means search bots can crawl them.
And they will crawl those links.
As a bonus, breadcrumbs also make life easier for your visitors. Sometimes, they’ll just want to go “up” a level or two and browse your website by following a different path.
Breadcrumbs for SEO
Mistake #39: You’re Not Implementing SSL
Neglecting to implement SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) on your website can lead to dire consequences.
SSL encryption not only safeguards the data transmitted between your website and users but is also a ranking signal for search engines. Websites with SSL certificates are trusted more by visitors and search engines alike.
Without SSL, visitors might be greeted with security warnings, which can erode trust and drive them away. By securing your site with HTTPS, you not only protect sensitive information but also bolster your SEO efforts and instill confidence in your online presence.
Mistake #40: Improper Use of a Trailing Slash
A trailing slash is placed at the end of a URL as a forward slash: “/” and is used to help define your website’s directory.
Previously, folders would have trailing slashes and files would not. But as we know, the world of SEO is always changing.

Trailing Slashes Don’t Matter After Domain Name
If your content can be seen on versions with and without trailing slashes, then the pages can be treated like separate URLs.
What does this mean for your SEO?
Duplicate content. In most cases, a canonical tag will specify the preferred version, so you won’t have to worry.
However, if different content is showing on trailing slash and non-trailing slash URLs, you’ll want to pick one version to index and redirect the other version to it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Technical SEO?
Search engines use a variety of ranking factors ranging from site speed and mobile-friendliness to make sure they’re indexing your site properly.
But if you’ve already created a winning keyword strategy, invested in content marketing, and developed a strong backlink profile, and still seeing your site not ranking as well as it should, it’s time to consider using a technical SEO service.
Technical SEO is the umbrella term that refers to a set of backend website and server optimizations that make it easier for web crawlers and visitors to understand and use your site. It’s the process of ensuring that your website meets all the technical requirements of search engines like Google with the ultimate goal of improving organic rankings. Optimizing your site for technical factors can also help offer an excellent user experience for customers.
Some of the most important elements include improving page speed, internal linking, usability, indexing, and website architecture.
2. What Are the Basics of SEO?
Successful SEO requires extensive know-how of how search engines work. And since SEO is a moving target, it takes time and practice to continually get it right.
You’ll be off to a good start if you understand the basics:
- Crawl accessibility to ensure search engines can read your website
- Persuasive content that addresses the searcher’s query
- Keyword optimized to attract both searchers and search engines
- An exceptional user experience that includes a fast load speed and well-designed UX
- Share-worthy content that earns links and citations
- Snippet/schema markup to stand out in the search engine results pages
3. What Are Some Common Technical SEO Problems?
Whenever you perform audits for your site, you’ll come across at least one or more of the following technical SEO problems:
- Canonical tag issues: The purpose of canonical tags is to tell search engines that a specific URL represents the main content of a particular page and thus, should be indexed.
- Duplicate content: This is content that appears on the web in multiple places.
- Blocked pages with robots.txt: According to Google, “If your web page is blocked with a robots.txt file, it can still appear in search results, but the search result will not have a description.”
- Incorrectly configured URL parameters: This can cause a multitude of issues, from creating duplicate content to wasting the crawl budget.
- Google Removal Tool: You can use this tool to remove third-party content from Google.
Additional issues can arise from pasting a noindex nofollow in the wrong area, indexing your content improperly, setting up international SEO incorrectly, setting up pagination incorrectly, and having ref link tags in the wrong place.
4. What Are The Components of Technical SEO?
Some of the most critical components of technical SEO include:
- Overall crawl of the website: If Google can’t crawl your website, your rankings will suffer.
- Fixing errors: From crawl errors to XML sitemap status, you want to make sure you can easily identify and fix any errors on your site.
- Page speed: No matter how good your content is, page load speeds can make or break a user experience.
- Mobile and desktop usability: While Google has historically crawled websites from a desktop point-of-view, delivering a mobile-optimized experience can earn you a green mark on Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
- Core Web Vitals: These are performance metrics that quantify key elements of the user experience.
- Review HTTPS status codes: If your site still contains HTTP URLs, users won’t be able to access your site, making implementing HTTPS a must.
- Keyword cannibalization: This takes place when you’re optimizing your home page and subpage for the same keywords, a practice most common with local SEO.
5. What Are the Top Technical SEO Tools?
The market is saturated with numerous technical SEO tools that can help with everything from keyword research and rank tracking to content optimization and backlink analysis.
Here are some of Ignite Visibility’s top picks:
- Google Search Console: A favorite among marketers, web developers, and website administrators, this is a free technical SEO service from Google (previously Google Webmaster tools) that allows you to monitor your site’s appearance and troubleshoot technical errors.
- Screaming Frog: With a customer base that includes Google, Apple, Amazon and Disney, Screaming Frog is one of the most popular tools for auditing technical issues on the market. The company’s SEO Spider quickly analyzes websites of any size and delivers specific technical SEO recommendations to users.
- Cloudflare: This free global CDN can not only speed up your site, but it can provide fast, cost-effective network services and protect your site from malicious attacks.
- Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test: Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test can verify how well a visitor can use your page on a mobile device, in addition to identifying specific mobile usability issues like small text, incompatible plugins, and more.
- GTmetrix: This performance analysis and reporting tool alerts you when any technical issues on your website arise that may impact site speed and user experience. GTmetrix also helps you visualize how page load times connect to total page times so you can determine the best strategy to improve the user experience for your visitors.
6. Are There Technical SEO Services?
To maximize your SEO campaign and drive traffic to your website, it’s imperative that you partner with a technical SEO service that will help you take on your competitors.
Luckily, there are plenty of companies that can do just that!
Ignite Visibility is one of them. We can address common on-page SEO issues like broken links, duplicate content, and missing alt attributes so you never have to worry about compromising your site’s performance.
7. Why is a Technical SEO Strategy Important?
Many marketers out there believe if your website has plenty of high-quality content and backlinks, that’s enough to get you to rank well.
The reality is that if you have the wrong technical SEO service or strategy in place, you can do a ton of damage to your site’s reputation.
Your site should be fully optimized for technical SEO for the following reasons:
-
- Influences how high you’ll rank in search results
- Impacts your site visitor’s actions and decision-making
- Affects your site’s conversion rates and sales
- Helps you compete with others in your industry
- Maximizes ROI from SEO
Time to Conduct a Technical SEO Audit!
Ultimately, conducting a routine technical SEO audit can lead to big gains when done correctly.
After all, if your organization is already investing its time, effort, and money into SEO, you want to get as much value as possible out of it. This involves frequent optimization, whether you’re managing the process in-house or enlisting the help of an SEO agency.
To the untrained eye, technical SEO issues aren’t easy to spot.
Hopefully, this list gives you a better idea of what to look for (and what can wrong) on the technical side of SEO.
If you suspect any of the above could be happening on your site, it’s time to have a long look at your site and your SEO efforts. If you still have questions, feel free to contact us.