Google Search Console, formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools is a mainstay in any SEO pro’s toolkit.
And while the tool’s been around for a while, it recently went through a major update, changing its entire interface and the reports it offers.
In this article, I’ll explain the benefits of Google Search Console, what’s changing in the new version, and break down each of the reports and how they’re used for SEO.
What You’ll Learn:
- The Benefits of Google Search Console
- How to Set Up Google Search Console For Your Site
- Google Search Console 2022: What Are the Latest GSC Changes?
- Google Search Console Top Tools 2022
- What’s Leaving Google Search Console?
- Google Search Console FAQs
The Benefits of Google Search Console
So what, exactly, does Google Search Console (GSC) offer digital marketers?
A lot.
- It informs Google about your online content. GSC lets you alert Google when you publish new content so it gets indexed faster.
- GSC lets you remove content from Google’s search index you’ve taken down from your website. That way, people won’t find broken links to your site in the search results.
- GSC shows you which search terms are drawing people to your website. That knowledge gives you the insight you need to optimize your site for relevant keywords.
- Search Console will also tell you if your site has malware or spam. That kind of warning can save your business.
- GSC will tell you if your product schema makes it into rich results. If not, you can take corrective action to ensure a better user experience.
- If you use accelerated mobile pages (AMP) GSC will warn you about pages that are non-compliant.
- Search Console shows you which websites link to yours. That will give you some insight into your popularity online.
- If any mobile users are having problems accessing your site, GSC will issue a notification to that effect. That way, you can make design changes to ensure a mobile-friendly experience.
The above features make Google Search Console an indispensable resource when it comes to SEO.
How to Set Up Google Search Console For Your Site
When you’re ready to set up Google Search Console for your website, you’re going to have to do some technical stuff.
It’s understandable if you’re not up to that task. In that case, you’ll have to hire a professional.
Start by visiting Google Search Console and signing in with your Google account.
Once you’re signed in, click “Add A Property” in the upper, left-hand corner.
Google Search Console “Add a Property”
When you do that, a pop-up will appear asking you to select either “Domain” or “URL prefix.”
Google Search Console: Selecting a Property Type
If you want to add your entire website, use “Domain.” Use “URL Prefix” for subdomains and other specified protocols.
Once you’ve typed in the site URL, click “Continue.”
Now you’ll need to prove ownership of the website you entered.
Google will show you the easiest method by default, which is uploading a simple HTML verification file to your site.
Once you’ve uploaded the file, click the confirmation link and Google Search Console will validate the existence of the file. Then, you’re all set up!
If, for whatever reason, you can’t upload a file to your website, you still have a few options to prove that you own the domain:
- An HTML Tag – put a meta tag in the homepage of your website
- Domain Name Provider – sign in to your domain name provider
- Google Analytics – use your Google Analytics code to validate ownership
- Google Tag Manager – use your Google Tag Manager account to validate ownership
You’ll have to use one of those five options to convince Google you’re the owner of your domain.
Set Up Owners, Users, and Permissions
To set up permissions in Google Search Console, go to “Settings” in the bottom-left corner.
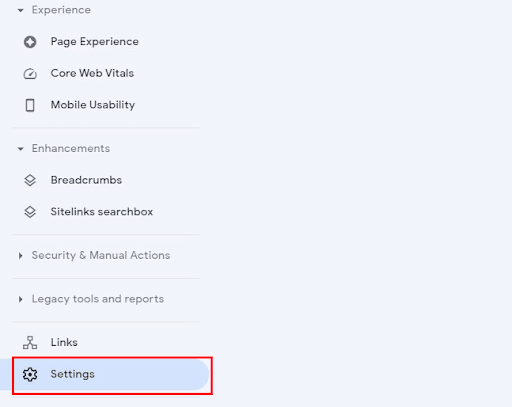
How to Set Up Permissions in Google Search Console
Then, select “Users and permissions.”
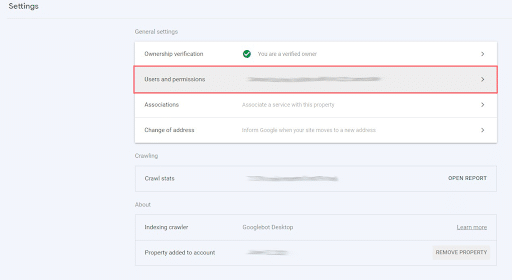
Add Users to Give Google Account Permissions
From there, you can select “Add User” to give any Google account permission to access that property.
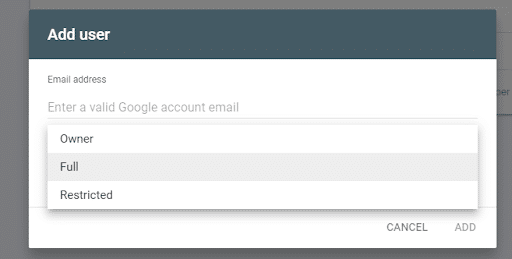
Adjust Permissions for Each Google Account
The “Add User” pop-up will allow you to adjust permissions for each account you add to the property.
How to Submit a Sitemap to Google Search Console
To submit your property’s sitemap to GSC, click on “Sitemaps” under “Index” in the left-hand menu.
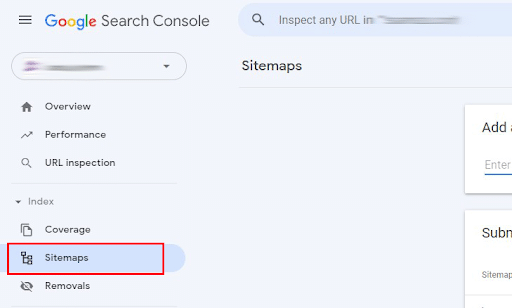
How to Submit Your Property’s Sitemaps
Then, all you need to do is paste the URL of your sitemap in the submission form.
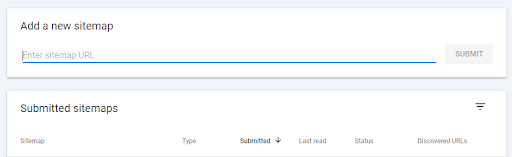
Adding a New Sitemap
Dimension and Metrics
Search Console has six performance dimensions to measure your site’s success in Google search:
- Queries: queries are search terms that generate impressions of your site page on Google
- Pages: Your top-performing web pages
- Countries: Top-performing countries for your website
- Devices: Shows how your site performs in mobile, desktop, and tablet searches
- Search appearance: Shows your site’s appearance in different rich results
- Dates: Organizes your clicks and impressions by date
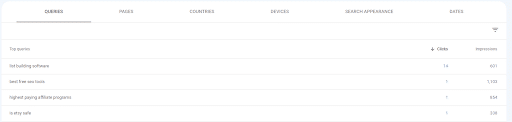
Example of Queries in Google Search Console
You can qualify those dimensions with four different performance metrics:
- Total clicks: The amount of clicks a page receives
- Total impressions: The amount of times a page appears in Google SERPs
- Average CTR: The average click-through rate a page earns
- Average position: How “high” a page appears in Google SERPs, relative to its closeness to the #1 spot
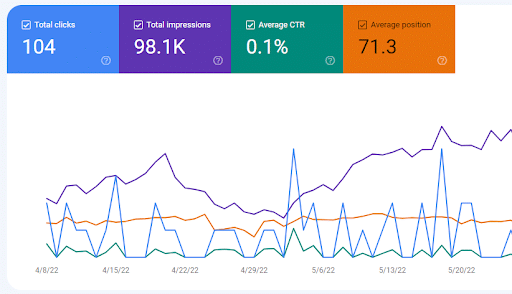
Inside Google Search Console
Filters
Search Console allows you to filter your performance with seven different criteria:
- Search type
- Date
- Query
- Page
- Country
- Device
- Search appearance
You can access these filters on the “Performance” page.
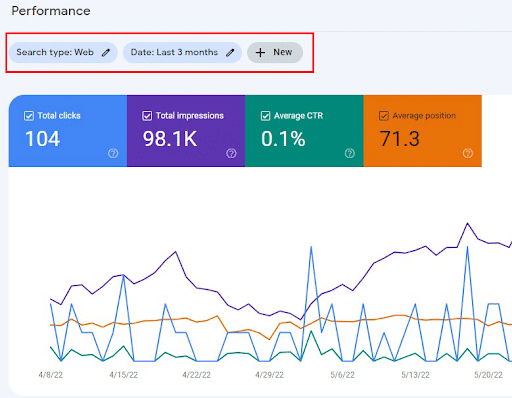
Google Search Console in 2022: What Are the Latest GSC Changes?
Search Console has improved in several ways this year:
Video Indexing
GSC has added a video indexing feature. If Google detects a video on your site, you’ll see a video indexing report under the “Coverage” section.
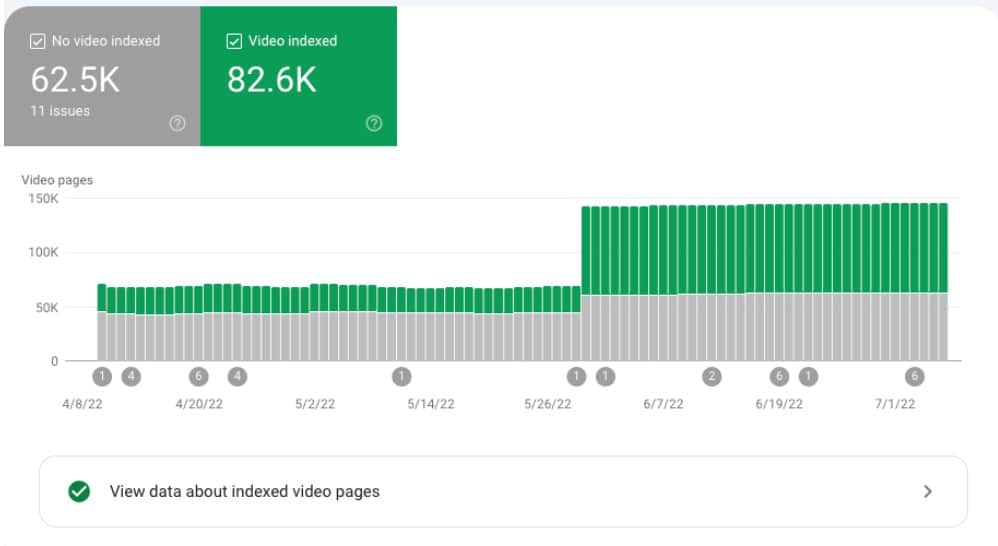
Google Search Console Video Indexing Report
Simpler Reports
Users told Google they felt confused about status warnings and were unsure if the warning affected the items’ visibility in search. In response, Google is separating statuses into two camps:
- Items that are valid, including those with minor issues
- Items with critical issues rendering them invalid
Google emphasized that there are no changes to indexing—only the way GSC reports it.
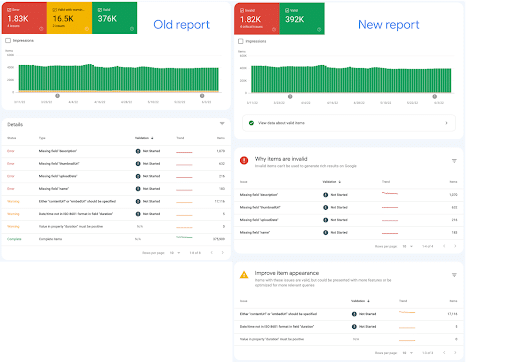
Simplified Reports: Comparing Old Reports to New Reports
URL Inspection API
Google released a URL inspection API to provide data for properties you manage—outside of Search Console. It’s a new tool for optimizing and debugging web pages more efficiently.
Google Analytics 4 Support
Until July, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) properties couldn’t use Search Console insights. Google fixed this by rolling out GA4 support for Search Console Insights.
Google Search Console Top Tools 2022
Search Console offers SEOs several game-changing tools for better performance in the SERPs.
Experience Reports:
GSC’s Experience section allows users to see how visitors experience their websites. The Experience section is divided into three reports we’ll discuss below.
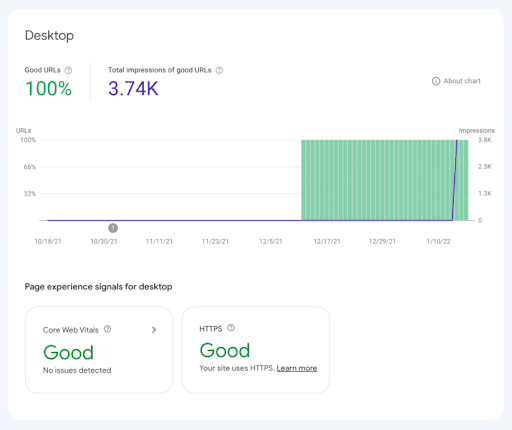
1. Page Experience
Page Experience provides a desktop and mobile report summarizing URL health on your site. Here you’ll see a percentage of “good” (valid) URLs on your site, plus their total impressions.
Page Experience also displays the status of your site’s Core Web Vitals and HTTPS.
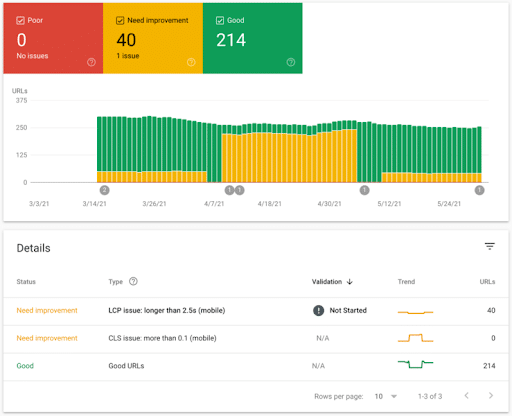
2. Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals (CWV) show your pages’ performance based on real-world usage. CWV consist of three primary metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): The amount of time it takes for the largest item on your page to load. Google considers LCP a vital page speed metric.
- First Input Delay (FID): The time it takes for your page to be useable. FID is a core metric of interactivity.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Visual stability of your page. With this metric, Google determines how dependable your pages are.
Core Web Vitals will tell you how your URLs perform in CWV metrics. GSC divides CWV metrics into three categories:
- Poor
- Needs improvement
- Good
3. Mobile Usability
The Mobile Usability report details your URLs’ “mobile-friendliness” in the eyes of Google. GSC divides mobile-friendliness status into two camps:
- Valid: Mobile-friendly pages, including those with minor issues
- Error: Pages that aren’t mobile friendly
Google openly acknowledges that mobile friendliness is a top-ranking factor.
You’ll need the Mobile Usability report to make sure all your URLs are mobile-friendly. If your pages are hard to use on mobile, you won’t rank high.
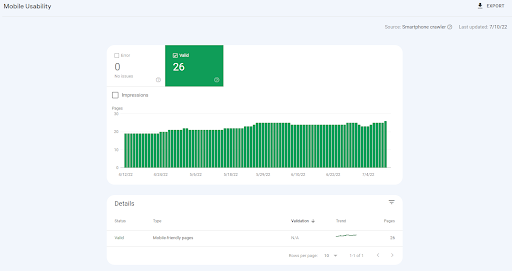
Mobile Usability
URL Inspection Tool
At the very top of the page, you’ll see the URL inspection tool.
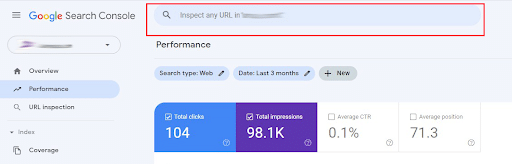
URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool has been available for quite some time and allows users to check the status of a particular URL to review how Google sees your page.
The status report provides information about your crawl history, as well as any indexing or AMP errors.
How it works is simple: just enter the URL in question and run the report.
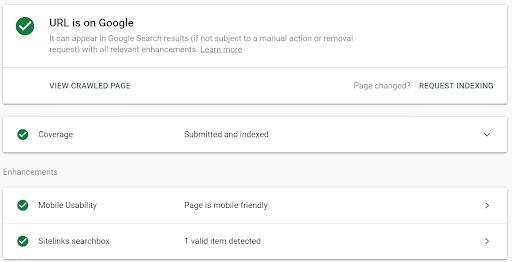
URL Inspection Report in Google Search Console
That said, there are a few things to keep in mind.
The URL must be part of the current property. Any URL outside of the property cannot be tested, even if you own that property. In that case, you’ll need to log into that account to check the URL.
The URL inspector can test both AMP and non-AMP URLs, and the tool will also provide information about the AMP or non-AMP version of the URL you entered.
If the URL entered has an alternate or duplicate version, the report will include the information for that page as well, plus information about the original version provided it’s part of a website you own.
The URL Inspection Tool replaces Fetch as Google, Crawl Errors and Blocked Resources reports that were previously available on the old version of Google Search Console.
The report can:
- Test indexed URLs: Retrieve the version of your page Google has indexed, and report on why or could or could not be indexed.
- Test live URLs: Test if a given URL can be indexed by Google; Google notes that this is useful when checking page updates against the version currently indexed.
- Request a URL be indexed: Request a certain URL be crawled and indexed (or reindexed) by Google; the process can take up to two weeks, and the status can be found in the report.
- View rendered version of a page: Shows how Google views your page.
Performance Report
The “Performance” report feature allows users to see how their site is performing in Google search.
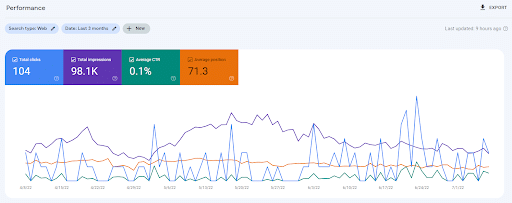
Example of Performance Report in Google Search Console
This report was introduced as a replacement to the old Search Analytics, adding an improved UI and access to more historical data.
Compared to Search Analytics, search marketers now have access to data dating back 16 months, as opposed to the three-month period offered before.
Use Performance reports to track metrics that reveal your average position, how often your site shows up, your click-through rates, and rich results, where applicable.
Performance reports also tell you how search traffic changes over time, which queries generate the most traffic, and where most of your visitors are coming from.
As of now, there aren’t many customization options built into the platform. However, users can pull data into Google Data Studio for more precise reports.
Hopefully, Google will continue to make changes to the report for faster access to vital insights.
Discover Reporting
As part of the Performance report, you can also check your site’s performance on Google Discover.
As a reminder, Google Discover is a solution for keeping up with your favorite topics.
If you have Google on your smartphone, you’ve probably noticed this feature on your mobile homepage. Discover typically shows users trending articles, human interest pieces, and content that relates to past search results.
On the publisher side, Google is making it easier to track your appearance and performance on Discover, through the new GSC Discover report.
Here, you’ll be able to review how often your site shows in users’ Discover feeds, how much traffic you’re getting, top performing content, and how Discover content compares with traditional SERPs.
Keep in mind that Discover reports only display for properties with a certain number of Discover impressions over the past 16 months.
Index Reports
Next on the left-hand menu, you’ll find the Index menu.
Here you’ll find three options:
- Coverage reports
- Sitemaps
- Removals
3 Options of Index Reports
Coverage Report
The Index Coverage Report replaces Index Status and Crawl Errors, combining the two reports to give you a comprehensive view of the crawling and indexing issues that can affect your site.
Here’s a quick rundown of what you can expect to find on the coverage page:
- Warnings: This lets you know if a page is indexed, but is blocked by robots.txt.
- Error: Scans for redirects, 404, robot.txt, and server errors.
- Valid Pages: Pages indexed by Google with no issues.
- Excluded Pages: Pages blocked on purpose (i.e. a noindex directive or a page removal tool) or by Google. Google might exclude pages if it detects duplicate content or some other problem.
Coverage reports show you the index status of your URLs, as well as any issues with your submitted sitemap.
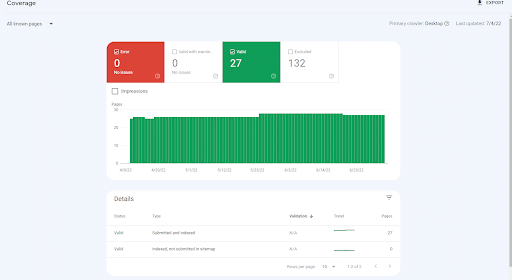
Coverage Report in Google Search Console
Sitemaps
The Sitemaps page shows you the status of any submitted sitemap for your property and if it contains any errors.
Once you’ve submitted your sitemap, check this page to check for errors. If there aren’t any errors, Google will submit all the links in your sitemap to its index. Again, that could take some time.
You can also submit new sitemaps on this page.
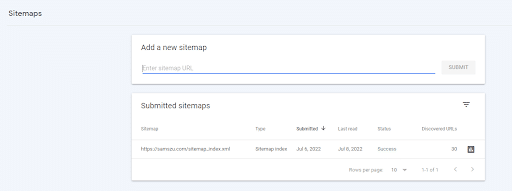
Submit New Sitemaps
Enhancement Reports
Enhancement reports allow you to review any issues related to structured data on your website.
You can find the Enhancements menu on the left-hand side of Search Console.
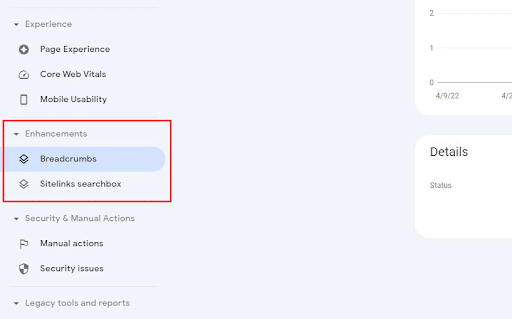
Google Search Console Enhancement Options
The Enhancements menu will only display enhancements that your site is eligible for. The site in the above example is eligible for breadcrumbs and sitelinks searchbox enhancement, so that’s all that displays.
Structured data is becoming a more significant part of SEO, and this report aims to help marketers understand more about what goes into the ranking criteria, rather than trying to follow Google’s EAT guidance as best they can.
You can find individual reports for the following rich results:
- AMP article
- Article
- Breadcrumb
- Carousel
- Course
- Critic Review
- Dataset
- Education Q&A
- Employer rating
- Estimated salary
- Event
- FAQ
- Fact check
- Guided recipe
- How-to
- Image License
- Job posting
- Job training
- Local business
- Logo
- Movie
- Product
- Q&A page
- Recipe
- Review snippet
- Sitelinks searchbox
- Software app
- Special Announcement
- Video
When looking at these reports, you want your current error count to be 0. If it isn’t, Google notes the increase in errors could be due to a change in your template, or mean that your rich results aren’t showing on the page.
If your report shows errors, you’ll want to investigate ASAP. Google goes into how to diagnose and fix a rich result error on this page.
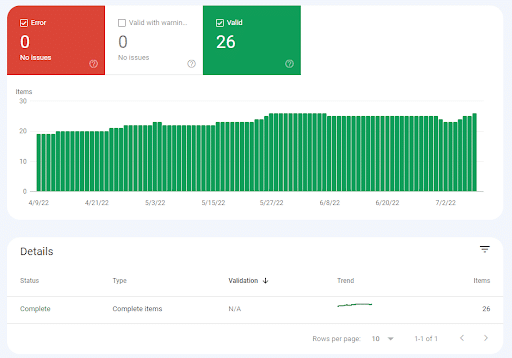
Updates to Structured Data/Rich Results in Google Search Console
Google is now showing Rich Results for product pages without structured data. Even if you haven’t created Structured Data for Google on a given page, Google interprets and presents Rich Results anyway.
So if you have an ecommerce site, you may see a rise in Rich Results impressions, even when you haven’t created structured data for those pages.
Security and Manual Actions Reports
Google created Security and Manual Action Reports to help you combat possible penalties or security issues.
You can find the Security and Manual Actions menu on the left side of GSC.
Manu
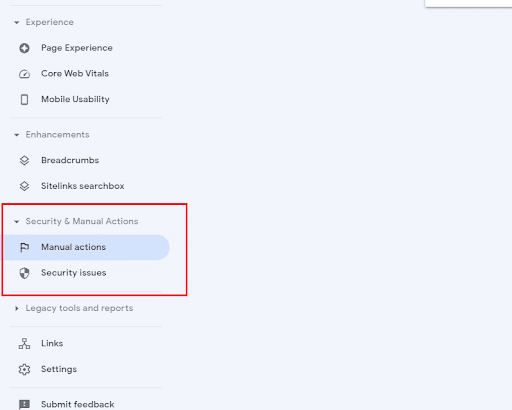
Security & Manual Actions Report
Manual Actions
As a quick refresher, Google issues a manual action when its human reviewers determine that pages on your website don’t comply with Google’s webmaster quality guidelines.
You can find Manual action reports under the Security and Manual Actions menu, though it’s not exceptionally detailed.
When Google hits you with a manual action, you can quickly scan the report for any problems, make the changes and request a review.
If all’s well, you’ll simply see a “no issues detected” message on the page to confirm you’re in the clear.

If no issues are detected, you’ll see this message in the Manual Actions section of Google Search Console
Security Issues
The security issues page will show you another report that you want to be brief.
Security Issues is located under Security & Manual Actions > Security.
Hopefully, you’ll see a big green check marking informing you that your site has no issues.
If not, you’ll see info about threats on your site. You’ll likely need to enlist the aid of an anti-virus specialist to take care of the problem.
Google Search Console Bubble Chart
Google’s created a template for Google Data Studio allowing you to visualize your Search Console data with a bubble chart.
To use Google’s bubble chart for query data visualization, connect your Google Search Console with Google Data Studios. You can connect GSC to Data Studios on the Connect to Data page.
Using the same browser where you just connected your Search Console account to Data Studios, open Google’s template.
Google will populate the bubble chart with sample data by default. You can replace the sample data with your own at the top of the page. Click on “click here to select your data,” and choose your data from Google Search Console.
After populating the bubble chart with your data, you’ll have a comprehensive view of your search performance.
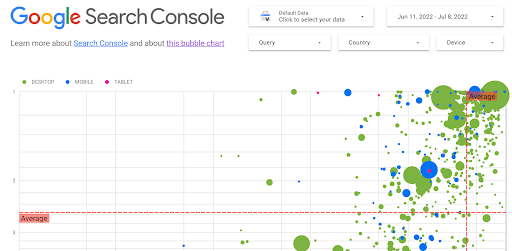
Google Search Console Bubble Chart
Links to Your Site in Google Search Console
Towards the bottom of the left-hand menu, you’ll see the Links report.
At the top of the report, you’ll see your top internal and external links. Scroll down, and you’ll see your Top Linking Text and Top Linking Sites.
Merging of User Management and Settings
Another improvement here is that user management and settings have merged, making it much easier to navigate through your admin features in the new interface than the fragmented old one.
The usability features in the new Search Console are much easier to navigate than they were in the old interface.
Restricted access has been renamed “read-only access,” meaning those users can read reports, without making changes. The benefit here is, you can give more employees access to Search Console Data while keeping peace of mind that they can’t mess anything up.
What’s more, you can also share reports with people who are not on your user’s list.
This is great for people who need to share performance results with a third-party stakeholder that they don’t necessarily want inside the system.
To share a report, all you’ll need to do is click the “share” found on the top righthand corner of the page featuring the report you’d like to share.
Direct Replacements
Some Search Console features are getting some minor updates, like a name change and an improved UI.
- Accelerated Mobile Pages will become AMP Status
- Sitemap reports are now just Sitemaps.
- Internal and external links are consolidated under one unified Links tab.
What’s Leaving Google Search Console?
Google hasn’t updated or replaced everything from the old Search Console.
Google has already bid farewell to Android apps, Fetch as Google, and Property Sets. They’ve also announced that HTML Improvements are on the way out, but haven’t set a retirement date.
HTML improvements was designed to alert you to on-page SEO issues like tagging and meta description problems, but given the changing nature of SEO, they aren’t especially useful anymore.
Google’s also disposed of the “Valid with warnings” index status. Index status is now separated into two categories:
- Valid: Pages appearing in Google Search, including those with minor issues
- Error: Pages with critical errors preventing visibility in Google Search
Wrapping Up: How to Use Google Search Console
Now you know how to use Google Search Console. Do yourself a favor: make it a habit to check it regularly. That way, you can monitor your site’s health and learn about search terms that are boosting your brand. That kind of knowledge will help you outrank your competitors.
Google Search Console FAQs
How Do I Connect Google Search Console With Google Analytics?
Google Analytics (GA) provides information about the people visiting your site. Meanwhile, Google Search Console provides you with technical information about your property.
Now, we’ll show you how to combine GA with GSC makes for a powerful insight machine. Before you begin, you’ll need to make sure your site is connected to both platforms.
- Go to your Google Analytics account, and click on “Admin” in the bottom-left corner.
2. Click on “Search Console Links” under “Product links.”
3. Choose the Console-connected domain you want to link to GA, select the web stream, and submit
Once done, GA will receive data from Search Console.
How Do I Use the Google Search Console API?
If you’re a power user who’d like to harvest key data from Google Search Console programmatically, you can do that. There’s an API available.
For starters, you’ll need a Google account to create a project in the API console.
You’ll also need to be somewhat familiar with how to use Google Search Console as a regular user. If you’re not familiar with it, check out our article above.
The Search Console API supports both Python and Java. You can read more about how to get started in the developer’s guide.
How Accurate Is the Data in Google Search Console?
Recently, some digital marketing professionals have called into question the accuracy of the data reported in Google Search Console.
About a year ago, Moz questioned the accuracy of GSC reports.
Some SEOs have conducted their own studies and noticed significant disparities between actual ranking data and what Search Console reported.
Bottom line: it’s not gospel. That’s why it’s best to use multiple tools to measure the effectiveness of your SEO campaigns.