Google SERP means: “SERP stands for Search Engine Results page. This refers to the pages of results that are returned when someone does a search in a search engine such as Google, Bing, Yahoo, Yandex or other.”
In this post, you will learn how search engine results pages (SERPs) work, as well as all their features.
What You’ll Learn:
- Introduction
- Traditional SEO
- How Google determines a page’s rank
- How SEO affects rankings
- The Evolution from SERPS to Result Features
- Overview of the major features
- How AI will affect the SERPs
- FAQs About Google SERP
What is a SERP?
SERP refers to a search engine result page. This is the page that appears when a user when types a search into Google (or any search engine).
Search results are generally triggered by keywords a user includes in a query.
But here’s the thing: no two results are the same.
Search engines work hard to customize the experience to each individual user, meaning that you’ll rarely see the same results twice – even using the same search engine.
You’ll also notice that search engines change with the times.
New search algorithms mean changing results, and updated features lead to the appearance of maps, images, videos, and more in your results.
And What Is Google Search Engine Results Page?
You’ll notice we put a lot of emphasis on Google.
Why? Because it’s by far the most dominant search engine in the space… by far.
You don’t even ‘search’ for something anymore. You Google it.
And you’re not alone.
As of May 2023, Google commanded 93% of all internet searches. Bing is the second most used search engine, coming in at only 2.8% of searches. That’s a huge difference and exactly why we focus so much attention on Google.
In fact, Google processes over 8.5 billion searches per day. Back in 1998, that number was just over 10,000 searches per day.
Google searches also dominate search traffic from mobile devices. Over 96% of US Google searches originate from a mobile device such as a cell phone or tablet.
Not only is Google clearly holding strong at the top, but it’s also increasing. And while any savvy SEO will focus their efforts in many directions, they know that when it comes to dominating the SERPs, Google is king.
What About Customized Search Results
Another benefit of using Google is that you’re able to customize your search results based on your past internet history.
This is beneficial for advertisers because, when the search results are targetting to users who have a history of interest in products or services similar to yours, it helps to curate a warmer audience.
And because users can opt out of their information being used to customize their search results, this option doesn’t come with any privacy concerns.
Traditional SEO – Organic vs. Paid Results
Traditional SEO usually refers to one of two things: organic or paid search.
Organic – refers to content that ranks high due to Google’s algorithm and a page’s optimization.
Paid results are paid by an advertiser to be displayed in a SERP.
The most effective SEO strategies combine both organic and paid SEO to achieve their business goals.
Organic Results
This is why you pay SEOs the big bucks – to take a page to the top.
An organic result appears because it’s relevant to a user’s search terms. Generally, the top spots are filled with the pages that most “naturally” suit a searcher’s query.
Because these are meant to be natural, there are no added bells and whistles.
Instead, these results are obtained through organic SEO.
Organic SEO refers to the methods used to get a high rank or placement on a search engine through the use of unpaid results.
Organic SEO caters to search algorithms by using keywords, backlinks, quality content, etc. (more on that shortly).
I won’t lie; it takes time and dedication to achieve top results through organic SEO. But it’s well worth it. Some benefits include:
- Generate more clicks overall – the top 5 organic listings on Google accounted for 67.6% of all clicks
- Because of content relevancy, organic results tend to keep top spots longer
- Build more trust with users, as most prefer to click on organic listings
- None of the extra costs associated with paid listings
Keep in mind, that your Google SERP position is likely to fluctuate based on algorithm updates and competing content.
Paid SERP Results
On the flip side, you have your paid results.
Paid ads work on a pay-per-click (PPC) basis, meaning an advertiser only pays when someone clicks on their ad.
And like organic results, paid results too have their fair share of benefits. While they may not have the same staying power, paid search can get you to the top and expose you to highly targeted customers – fast.
And though they may not see the same CTRs as organic listings – on average, Google PPC ads see between a 4-6% CTR – those that do click are often ready to convert.
Beyond that, paid results come with a set of analytics that will tell you everything from clicks and impressions to conversions and ROI.
Powered primarily by keywords, paid results also provide these additional benefits:
- Appearing in prime page real estate, usually at the very top of the page or on the side.
- Matching paid results closely to any keyword a user enters in their search.
- Looking almost identical to organic listings – minus a small “ad” or “sponsored” badge.
- The ability to see different ads suited to different niches.
- Requiring the advertiser to pay only when someone clicks on their ad. This is called pay-per-click or PPC.
As mentioned above, paid ads can be customized depending on each niche.
For example, retailers can show off pictures and prices of their products through Shopping Ads.
Google Ads extensions have also opened new doors for advertisers. Now, local businesses can include location extensions, those with downloadable apps can include app extensions, and any business can include sitelink extensions with additional links.
In addition, the insights you gain through your paid analytics can help inform the decisions you make when it comes to organic SEO as well, which is why the two often work so well together.
|
If you’re aiming to enhance your paid search strategy further, consider leveraging residential proxies to diversify your online presence and reach your target audience more effectively. Residential proxies provide a layer of anonymity and help in overcoming geographical restrictions, ensuring your ads reach a broader and more diverse set of potential customers.
How Does Google Determine a Page’s Rank on a SERP?
There’s no easy answer to this one.
The websites on the first page are the ones Google has determined to be the most relevant and useful to a particular search query.
To make that decision, Google relies on a complex algorithm of 200+ ranking signals (for a full list, look here).
In technical terms, the process works something like this:
- Google uses its Googlebot (search bot software) to crawl a site. “Crawling” is the process where the bot goes to different sites to find new information. The Googlebot finds sites to crawl through links.
- The information gathered by the Googlebot is then indexed. This is where Google uses those 200 ranking factors to determine the placement of a site in the SERP.
So in order to rank high, companies cater to the ranking signals and algorithms through SEO practices. While there are a number of ranking signals you can focus on, some of the most important ones include:
- The relevance of your domain
- The usability of your website
- The authority and expertise of your domain
- The number of backlinks to your website
- Your reputation in your industry
To make it simple, focus on EEAT – experience, expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. When you produce quality content that searchers enjoy, Google will take notice and start to boost your results to the desired top spots.
How SEO Affects Search Engine Results Page
SEO efforts are separated into two categories:
- On-page SEO – refers to all the factors you control on the page such as linking, content optimization, page titles, etc
- Off-page SEO – includes all factors off-page, such as social media networking, blog promotion, etc.
Think of it this way: on-page SEO has more to do with what your page will rank for, while off-page is more concerned with where your page will rank.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is how you optimize your individual web pages.
This refers in large part to the content of a page – which may be the single most important factor when it comes to determining a page’s rank.
Good content is relevant, relatable, serves a clear purpose to your audience, and is linkable.
It’s generally focused on a very specific subject, clearly stated through the use of specific keywords.
Use these keywords several times throughout your content, as well as in:
- Your title tag
- URL
- Image alt text
- Meta descriptions
- Headings and subheadings
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is any SEO effort that happens away from the actual webpage.
When done correctly, it signals to search engines your site is popular, relevant, and trustworthy.
Most commonly, this is done through backlinks.
Backlinks are links from other web pages that lead back to your site. The more quality backlinks you can accrue, the more likely Google is to trust your site and rank it accordingly.
But there’s more to off-page SEO than backlinks, such as:
- Social media marketing
- Influencer marketing
- Guest blogging
- Events, giveaways, etc.

On-Page SEO vs Off-Page SEO
Technical SEO
It would be remiss of me to not mention the importance of technical SEO.
While this can fall into either on or off-page, it’s often presented as its own category because it refers to what happens behind the scenes.
Some of the most important technical SEO factors include:
- Page load speed
- Duplicate content
- Sitemaps
- Rel=canonical issues
- Mobile optimization
- Broken links
- Internal linking structure
You can learn more about technical SEO and how it affects your site rank in our comprehensive guide.

Technical SEO Factors
The Evolution From SEO to Result Features
When the internet burst onto the scene in 1991, we never could have imagined where we would be today. With all of the changes that came after that very first website, SEO also had to make an evolution.
In fact, Google wasn’t even the first search engine. Excite was. Back in 1993, Excite laid the foundation for internet cataloging and searching. Yahoo entered the industry in 1994 and Google turned up in 1997.
Back in the day, SEO was pretty spammy. Tactics like keyword stuffing, spammy backlinks, and over-tagging were the lay of the land. It also often took months for these black hat tricks to even work.
Google eventually got tired of letting these spammy tactics work and started to brainstorm how to revolutionize the SEO industry. Around 2003, the search engine mega-giant started to penalize spammy sites for keyword stuffing and using bad links. They also introduced the idea of local SEO to help brick-and-mortar stores gain more foot traffic.
Around 2006, Google really started to put its user first by promoting sites that were more user-centric. In 2008, popular tools such as Google Trends and Google Analytics became available. This helped advertisers to understand how to make content that their audiences actually wanted to see.
In 2010, we started to see Google get stricter on things like keywords, over-optimization, and content quality. They also introduced new features whose goal were to help improve accessibility and social connections while also satisfying the public’s growing curiosity about a variety of topics.
Things like quality backlinks and social media sharing started to become more important, as Google relied on the public and others in the industry to help them determine which sites could be deemed as “experts.”
Today, there is so much more to SEO than just organic and paid results.
In fact, Google offers an impressive variety of ways to push your page to the top.
We call these SERP features, and they’re changing the game for SEO.
Traditional, HTML SEO listings are no longer the best and surest way to rank high.
Instead, Google searchers are increasingly looking to results like videos, featured snippets, and map boxes to quickly answer a search query.
This doesn’t mean that SEO is over. The opportunity is still there, but the way we approach it is changing.
Rather than “I want the top listing!”, brands need to be thinking: “I want the featured snippet” or “I want to show up in the video box” – and plan their SEO strategy from there.
To do so, SEOs need to focus their attention on answers, rather than results.
An Overview of Major SERP Features
There’s no shortage of SERP features, and generally, a feature will have some sort of unique image, map, or border to signal it’s different from the rest of the listings.
Some features generate simply through your content, while others require additional information through structured data.
Google separates its features into two categories, as explained below:
- Content type: Many search features are tied to your page topic. For example, if the page has a recipe or a news article, or contains information about an event or a book. Google Search results can then apply content-specific features to make your page eligible to appear in a top news stories carousel, a recipe carousel, or an events list.
- Enhancements: These features can be applied to more than one kind of content type. For example, providing review stars for a recipe or movie, or exposing a carousel of rich results (previously known as rich cards)
Some of these important features include featured snippets, top and bottom ads, carousels, People Also Ask boxes, Local Packs, Knowledge Panels, Top Stories, and more.
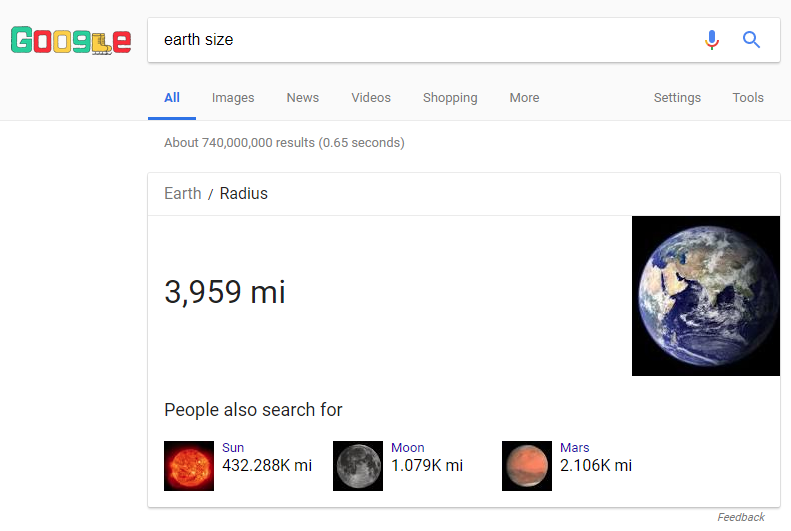
Featured Snippet
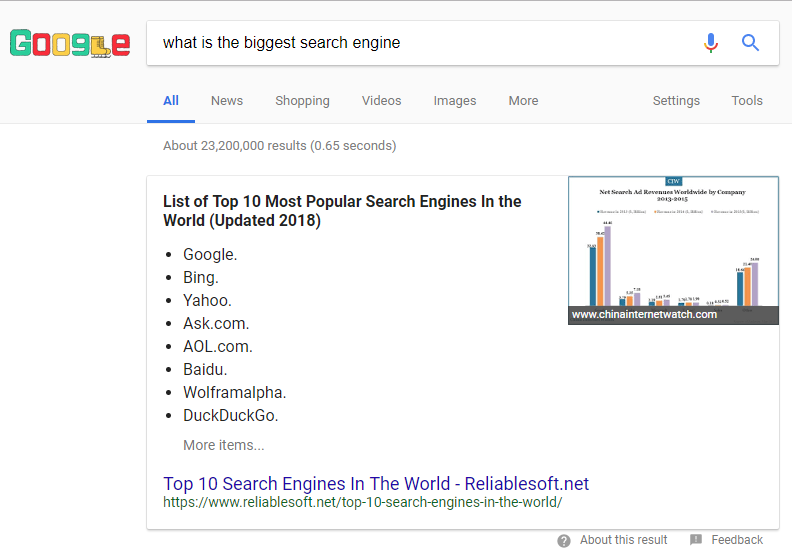
We call this Google SERP position number 0, and you may have guessed, that they’re a pretty big deal. A Google SERP snippet preview is a surefire route to conversions.
A featured snippet appears above the top spot. It’s pulled directly from a webpage that provides a specific answer to a searcher’s query.
For example, if you type “what is the biggest search engine” into Google, you’ll see this featured snippet at the top:
Google SERP Snippet Preview
To rank for a featured snippet you should already be within the top 5 positions and focus primarily on finding common questions your audience asks and providing clear answers.
Top and Bottom Ads
Top and bottom ads are exactly what they sound like. They’re the ads on the top and the bottom of the SERP.

In this example, you can see Adobe’s top ad. It’s clearly marked as “Sponsored” and it’s above every other search result, including the featured snippet.
On the other side, the example below shows you a bottom ad.
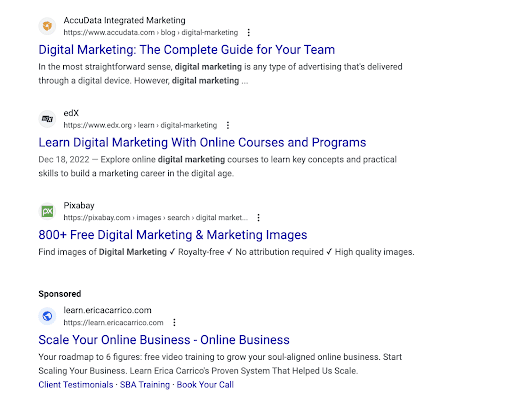
This ad appears at the very bottom of the SERP, below everything else. It’s used to capture those searchers who scroll to the very bottom of the page before reading anything else.
Carousels
Carousels are list-like displays that appear in a row.
Here’s what a recipe carousel looks like:
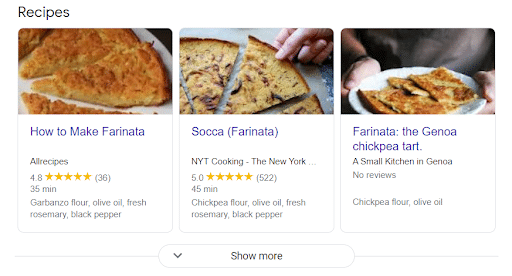
To reach carousel status all items must already be in a list form and follow standard structures markup guidelines.
Google has recently updated its movie carousels to show where you can stream the movies (including popular platforms like Netflix, Hulu and HBO, but also little-known streaming services for offbeat films).
Stay-at-home orders and social distancing may have pushed the search engine to make updates in the movie department quicker than they otherwise would have.
People Also Ask or Related Questions
This one appears as a dropdown box under People Also Ask.
It usually contains four questions, and when clicked upon, will show a brief snippet, as well as two new related questions.
For example, If I ask Google “how to train a puppy,” it will give this list of related questions right under the featured snippet:
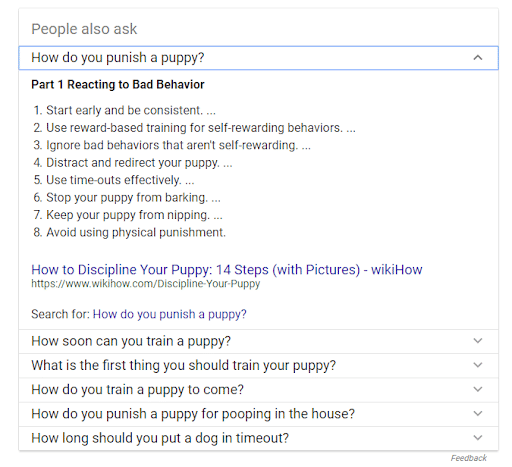
These questions and answers pull from different sites, and sometimes, all from the same site (which represents an incredible SEO opportunity).
To rank here, you’ll need to already rank in the top search results. Make sure to focus on Q&A and FAQs in your content to increase the odds that your snippet will get pulled.
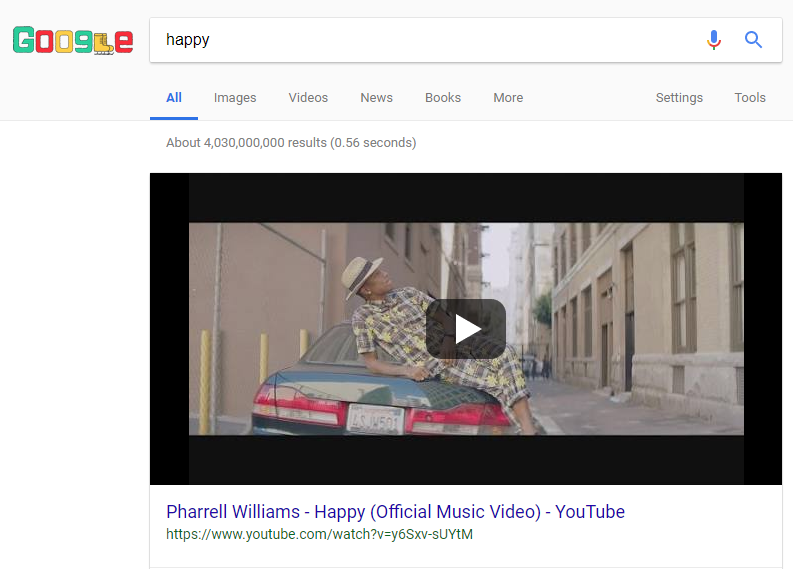
Video Feature
Video results can appear as a thumbnail in searches. They’re connected to a specific keyword and usually come from YouTube.
For example, type “happy” into Google. You’ll see this video on the first SERP:
Google Video Feature Example
You can provide details such as the description, thumbnail URL, upload date, and duration.
These days, one of the few ways to get your video to appear as a snippet is through hosting on YouTube. So make sure you’re using YouTube if you have a video strategy, and optimize all videos correctly.
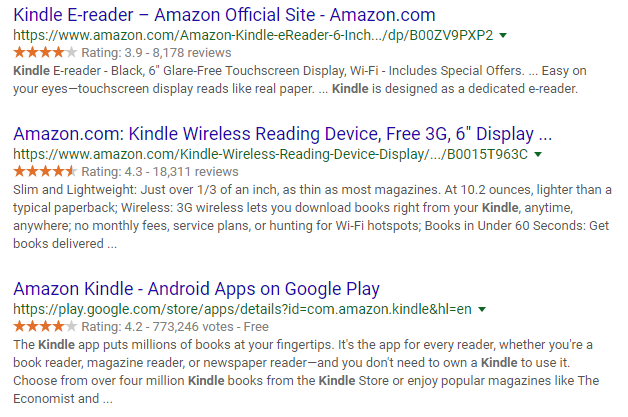
Reviews
Reviews are most often displayed as stars (1-5) and are shown primarily for products, recipes, and related items. They appear directly below title and URL, and generally receive higher click-through rates than those without.
So, if you type Amazon Kindle into Google, you’ll see this result with a starred review:
Google Reviews on the SERP
There are two types of reviews allowed by Google:
- Critic Review – a snippet from a longer review, used for local businesses, movies, and books
- Review Snippets – a rich result collected from a review website, used for local businesses, movies, books, products
To use them, you must implement schema.org and follow the guidelines provided by Google.
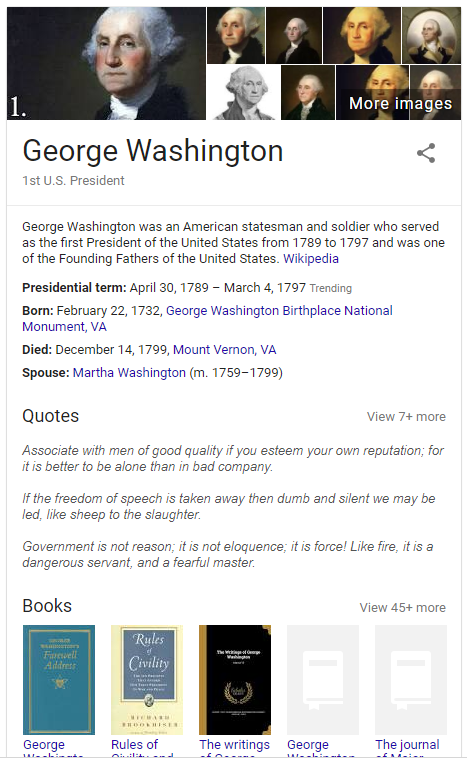
Knowledge Panel
The knowledge panel offers a searcher a broad overview of information about local businesses, corporations, well-known people, movies, etc.
For example, this is what comes up in a search for George Washington:
Knowledge Panel Google
The information displayed in the knowledge panel can pull from one or more sources and typically appear to the right of search results on desktops, and at the top of results on mobile.
Though similar to a featured snippet, a knowledge panel typically includes more variety of information. It’s powered by Google’s Knowledge Graph – a database that pulls information from trusted sources.
Instant Answer
An instant answer (also called the ‘answer box’) shows when Google can provide a short, concise answer to a question.
Unlike featured snippets, they provide no detail or description outside of the actual answer.
Instant Answer SERP
The Knowledge Graph also powers Instant Answers, which means there’s little in terms of SEO that most businesses can do to achieve an Instant Answer result.
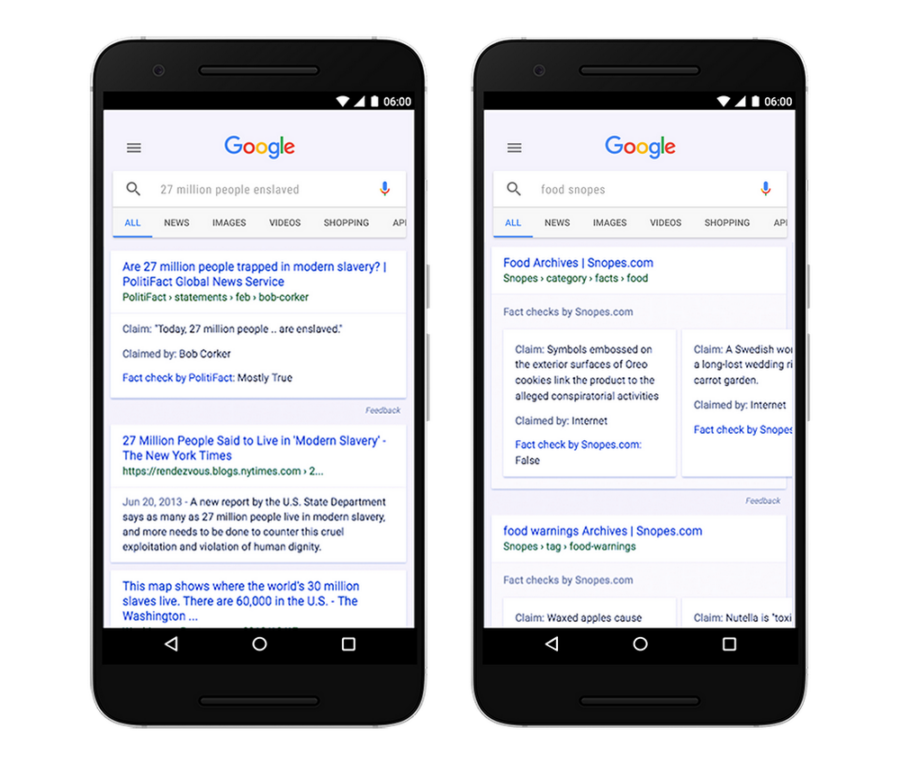
Fact-Checking
Google allows SEOs to implement a fact-check schema called ClaimReview. The result is a confirmation from a reputable source on whether the claim is true, false, or somewhere in between.
ClaimReview Fact Check Schema Sample from Google
Using fact-check schema can help solidify your rank in Google because it provides legitimacy to your site. That’s an invaluable asset to have on your team.
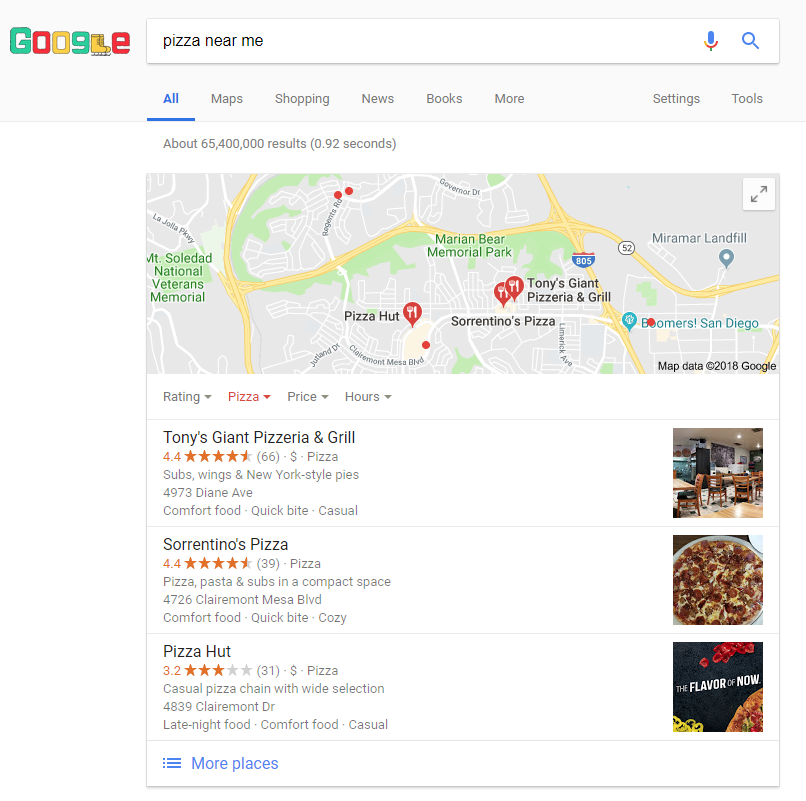
Local Pack
A local pack will show in a SERP for, you guessed it, local searches. Those include searches with local intent or those that include a business or location name.
That means if I type in “pizza near me,” Google will pull the following local pack:
Google SERP Local Pack
The pack usually includes a map with various location pins and the top three locations.
Clicking on the map will expand it and offer more location suggestions along the side. Clicking on one of the individual locations will pull up a knowledge panel.
Local packs are extremely important for any local business. To land in the local pack, you’ll need to claim (and optimize) your Google Business Profile and emphasize local SEO.
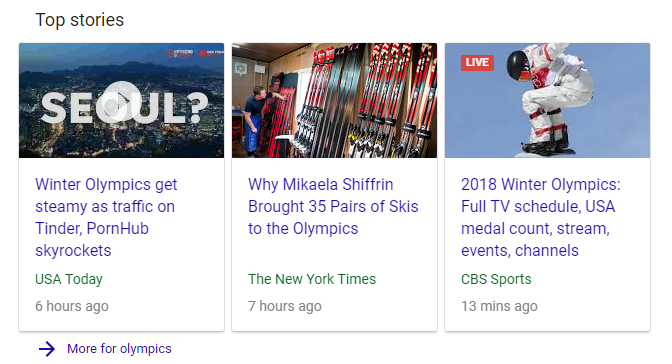
Top Stories
Top Stories usually appearing response to a news search query, as a carousel of articles most relevant to the topic. The stories typically appear at the top of the SERP and come in a block of three.
For example, a search for the Olympics, will provide this:
Google SERP Top Stories
In order to stay on top of Top Stories, articles must be time-sensitive and provide updated, consistent information.
While Top Stories have very good CTRs, they’re usually reserved for bigger news organizations.
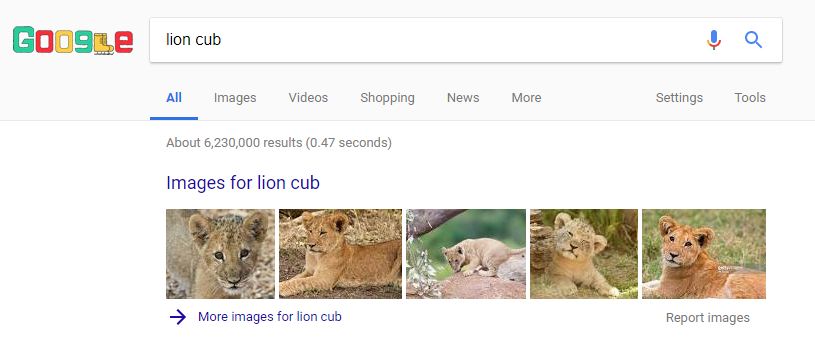
Image Pack
Image packs appear at the top of the SERP when a keyword entered in the search query triggers specific images as well as text results.
A search for “lion cub” would produce something like this:
Image Pack Example
You can increase the likelihood of appearing in an Image Pack by optimizing your images for related keywords.
The downside is that clicking on one image takes a user to the Google Image results, not directly to your website. To get there, the user would have to click the photo and the given URL.
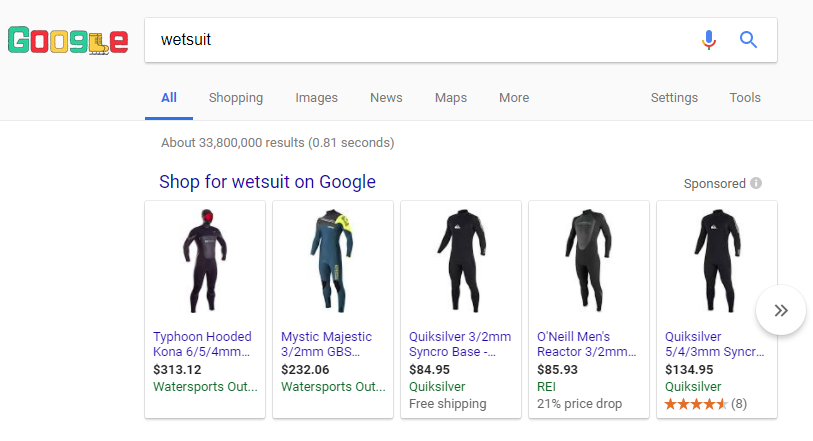
Shopping Results
Shopping Results (or ads) are rich results that feature a thumbnail image, its title, price, link to a product page, and sometimes its review rating.
They appear at the top or to the right of the SERP:
Google SERP Shopping Results Feature
They’re best for businesses with over 500 products (Google favors those with more), who can point searchers to a high-quality website.
Organic Listing FAQs
You can use schema markup to give the search engines a little more information about your website in a way that’s invisible to your users.
For example, if you’d like to identify the author of an article, there’s a schema type called Blog that includes an author property. You’d set the name of the author for that property.
Why would you want to go the extra mile to use FAQ markup in addition to standard HTML markup? Because it makes it easier for search engines to parse the content on your site, ultimately landing you a spot on the Google search engine results.
That’s important because their algorithms might use that additional info to give your web pages a higher rank in the search results.
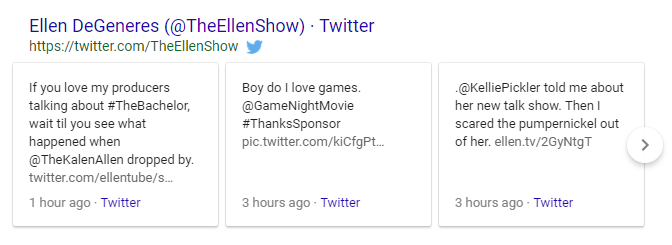
Twitter Cards
This one’s a little different from the others, as it doesn’t come directly from Google. Rather, Twitter packs are a short collection of recent Tweets related to a searcher’s query.
Twitter Pack SERP Feature
They usually come in sets of three and appear about halfway down the page.
These can come from verified or unverified accounts, and the specifications for how to appear in a Twitter pack are still somewhat unclear.
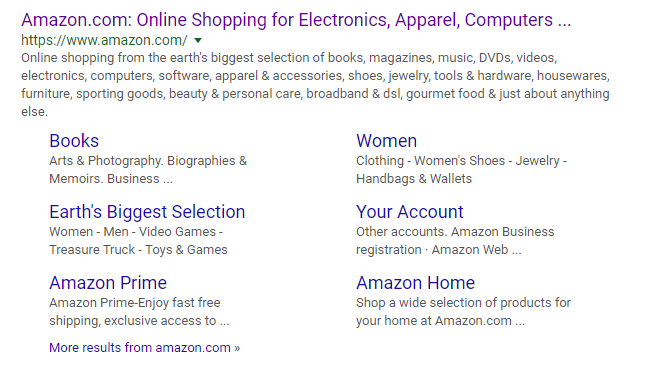
Sitelinks
Sitelinks allow you to enhance your existing listing by adding other relevant links to your site below your result.
Amazon’s looks like this:
Sitelinks Feature
Sitelinks can be extremely beneficial in helping users navigate your site and finding spread traffic throughout. Think of it as a way to occupy multiple spots in the SERP, while only really needing one.
To get sitelinks added, you need to have a decent amount of traffic. Beyond that, make sure you have a solid internal linking structure and schema markup on your site.
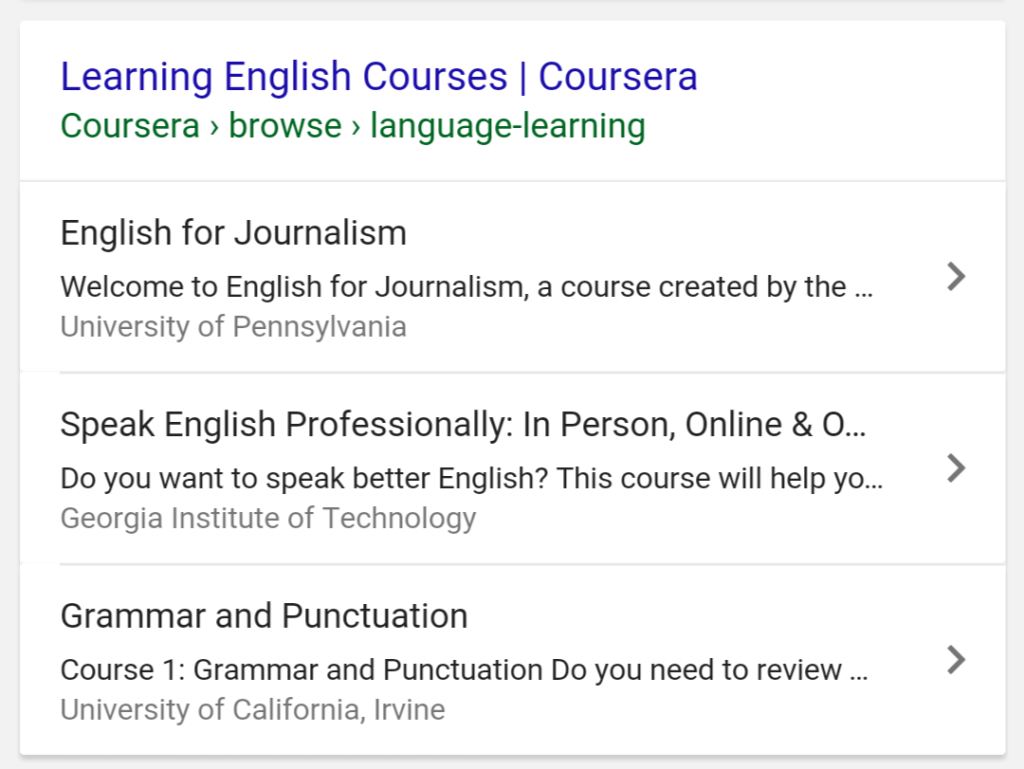
Courses
Online learning has taken off. We see sites like Coursera and Udemy all over the place, and now Google even has its own courses through Google Analytics Academy, Google Skillshop, Google Digital Garage and more.
If you offer courses on your site, use structured data to showcase them right from the SERP.
Google SERP Courses Structured Data
The image above is a mobile version, and it’ll look slightly different on desktop.
Once you add the required properties, you can validate your code using the Rich Results Test.
Search Box
This one goes hand-in-hand with sitelinks, but gives users the additional option of searching your content right from the SERP page.
To use one with your search results, you’ll first need to have a search engine on your website (these are common; most sites already have a search feature for their content).
These boxes have obvious benefits for both users and brands; it makes it easy for anyone to search and locate desired content, without having to sift through any unnecessary pages or links, which in turn will decrease bounce rate.
Breadcrumbs
Help users (and Google algorithms) navigate your site more easily by setting up breadcrumbs (seen in the green text in the image below).
Google SERP Breadcrumb Example
There are two ways to set breadcrumbs for your site:
- Update your URLs manually
- Hardcode breadcrumbs into your site’s design
Again, this is a form of structured data that you can implement using the required properties and validate using Google’s Rich Results Test.
In-Depth Article
These can be tricky to spot. They appear along with organic listings, with little to no distinguishable characteristics to separate them.
Typically, you’ll find them towards the bottom of the SERP and provide particularly lengthy pieces about a given search topic.
To appear here, you’ll need schema markup as well as:
- Long-form content (2,000-5,000 words)
- High-quality writing
- Optimized headlines, images, descriptions, etc.
Because they’re hard to spot and appear so low. there isn’t as much value associated with in-depth articles.
How AI Will Affect the SERPs
By now, you have certainly heard how Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the landscape for the future of everything from media marketing to yes; you guessed it, SERP.
So what does all this AI stuff mean for search results?
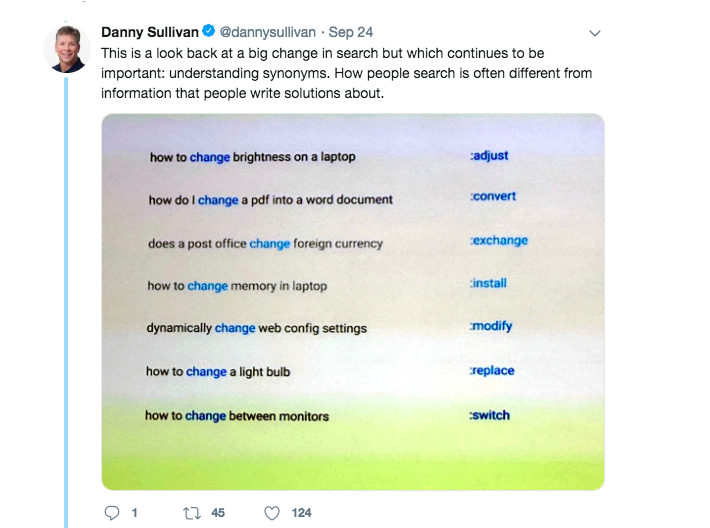
Neural Matching
For starters, let’s look at “neural matching”. This is an algorithm that uses AI technology to help analyze and understand language (specifically synonyms) better to give users more diverse search results.
Google’s using AI to match synonyms
Image and Video Search
Given the importance of image and video, Google recently rolled out new features that “use AI to make your search experience more visual and enjoyable” says Director of Google Engineering at Google Images, Cathy Edwards.
Google’s primary focus is user experience. With that, SERPs will have more appealing and useful content, video previews and image searching for their users. The search engine is also moving toward AI-powered technology that will make it more visually appealing, natural, and intuitive to explore information.
Dynamic Search Results
Dynamic search results are another awesome and useful search component – it uses AI to help you make your search experience easier.
Even if you don’t know exactly what you’re searching for or what you may need to search for after your initial search, Google shows you subtopics at the top of the page that apply relevant to your query.
Dynamic Search Results in the SERPs
AI Generated Content
In addition to using AI to improve its algorithm and indexing efforts, Google is creating tools to detect AI-generated content.
Over the past decade+, Google has made it clear that high-quality, user-friendly content is king. With more and more content creators turning to AI, Google is improving the way they review content. While AI can be a great thing, it can also produce some content that is not so great – or even truth.
Google recently released a blog where they state that “using automation – including AI – to generate content with the primary purpose of manipulating ranking in search results is a violation of our spam policies.”
Basically, use AI as a tool to aid in your content creation process but, at the end of the day, Google is going to continue to require that human touch.
FAQs About Google SERP
1. What are some top tools?
If you’re in the market for a great Google tool, you’ll be happy to learn that there are plenty of them on the market that will help you track and improve your website’s rank. Here are some of the best:
- SERPBook: An oldie but a goodie. It will show you where your website ranks for specific keywords on all the major search engines. Additionally, it will chart your rank history over time. That way, you can see if there’s an improving trend. It also offers automated, white-label reports.
- STAT: Wonder if any of your keywords made it to the answer box? If so, check out STAT. You can also use it to track rank, gain competitor intelligence, and optimize for Local SEO.
- SEMRush: A tool that just gets better over time. SEMRush lets you plug in any keyword and it will show you the top-ranking websites. It will also give you a Keyword Difficulty rating so you can see how hard (or easy) it will be to rank for a specific search term.
- SEOquake: Unlike the other tools mentioned here, SEOquake is a browser plug-in. That means you can use it to analyze websites and search results while you’re surfing the web. In fact, SEOquake offers real-time stats beneath every search result. That kind of info will help you get ahead of the competition.
- Google’s Rich Results Test: One way to stand out is with a markup that highlights key details, such as star ratings, publication dates, and price info. However, it’s easy to make mistakes when adding markup. Use Google’s Rich Results Test to uncover any structured data problems so you can fix them.
- Schema App Structured Data: Speaking of markup, you can easily add it to your WordPress site with the Schema App Structured Data plugin. As with most plugins, it enables you to update your website even if you don’t know how to code.
- Ahrefs: Looking for an all-in-one tool that’s often billed as the “Rolls Royce” of SEO services? If so, then check out Ahrefs. It’s a bit pricey but offers several features that will help you get a great rank.
- Google Search Console: What’s not to love about a free tool offered by the Big G itself? Google Search Console is a great place to start if you’re looking for info about keywords people use to find your site, how many times your site appears in search, and info about the technical aspects of your web pages.
- Answer the Public: If you’d like to generate a FAQ that will rank in search, take a look at Answer the Public, a website that accepts a keyword and generates questions from it. You can use those questions in your own content.
- Majestic: Identify websites that are great candidates for backlinks with Majestic. It’s a tool that will give you insights into the “link juice” that other websites can offer. You can also learn quite a bit about your own website with the tool, such as which backlinks you need to disavow.
2. What Are Google Rank Checker Tools?
When it comes to SEO, it’s important to know where your keywords rank in the search results. If you’re tracking several dozen or several hundred keywords, it’s not practical to Google them every day and scroll to find out where your search listings are located.
In fact, Google won’t let you perform too many searches in a single day. Your IP address will be blocked.
That’s why it’s important to use rank checker tools. They’ll monitor keywords on your behalf and show you where your site ranks for each one of them.
Even better, many rank checker tools will show you where your keywords have ranked over time. That way, you can see if the trend is your friend.
3. Where Are Good Places to Get Search Marketing Education?
There are several great resources online:
- Ignite Visibility Blog: Our own blog here at Ignite Visibility has an SEO Starter Guide, info about the latest Google algorithm updates, and news about all the latest trends in digital marketing.
- Moz’s SEO Learning Center: If you’re new to SEO, Moz’s SEO Learning Center contains a library of information about ranking, visibility, on-site SEO, building a backlink profile, Local SEO, and keyword research.
- Google Webmaster Central Blog: Google shares all the latest news about its search engine on the Webmaster Central Blog.
- Search Engine Journal: One of the most popular blogs that share all the latest news of interest to the search community.
4. How important are Google SERPs to the success of my website?
Google SERPs are extremely important to the success of your site.
Most people who search for keywords click on a site that comes up on the first page of the search results. If you’re looking to increase your organic traffic, you want to increase your odds of being within the top 5 results on the very first page.
5. What affects my SERP ranking more, on-page SEO or off-page SEO?
Both types of SEO are very important to your ranking.
Anything you can do to increase Google’s ability to successfully crawl your site, the better. It all plays a role in how your site ranks.
6. All of this is over my head! Is there someone I can hire to improve my SERP ranking?
Of course! While it is possible to learn how to increase your ranking on your own, there are many qualified digital marketing consultants and agencies who know the ins-and-outs of Google SEO.
They can improve your page’s SEO and increase your likelihood of ending up in one of the coveted top 5 spots. Just be sure to vet them carefully before you hire them. Ask for samples or case studies to prove their work’s success.
Wrapping Up with Google SERP in SEO
Ignite Visibility is home to a team of expert SEO marketing professionals. We specialize in leveraging the power of SEO campaigns to help businesses drive targeted traffic and achieve their marketing goals.
Whether we are increasing your website rankings by optimizing on-page performance or backend issues, we handle every aspect of SEO marketing to ensure our clients receive optimal results.
Want to learn more about our SEO marketing services? Contact us for a free proposal!