Want to take control of how search engines crawl your site? With ‘robots.txt disallow,’ you’re in charge of what stays private.
As Seth Kluver, AVP SEO/GEO, emphasizes, mastering this file is key to ensuring your site gets indexed just the way you want it.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize your site’s crawl strategy, you need to familiarize yourself with robots.txt disallow.
What We’ll Cover:
- What Is A Robots.txt File?
- Examples of How to Block URLs in Robots.txt
- Handling Resource Files and Crawl Budget Optimization
- Getting Started With Robots.txt
- How to Test Your Results
- Modern SEO Practices: Crawl Budget Management
- Robots.txt + JavaScript & SPAs: Let’s Get Technical
- Robots.txt for Different Search Engines
- Avoiding Robots.txt Mistakes Like a Pro
- Robots.txt FAQs
What is a Robots.txt File?
Robots.txt, also known as the Robot Exclusion, is key in preventing search engine robots from crawling restricted areas of your site.
How Robots.txt Works
Robots.txt is a text file that webmasters create to teach robots how to crawl website pages and lets crawlers know whether to access a file or not. This element can effectively manage crawler traffic, indicating what to crawl and what to ignore.
Purpose of Robots.txt
A robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to ignore and helps to direct them to the pages of importance. This helps optimize your crawl budget and ensures your page is properly indexed. This improves your site efficiency and benefits your SEO strategy.
Be careful not to block important sites, as this could unintentionally lower your ranking on a SERP.
In addition to blocking certain pages, you can also use it to prevent specific audio, video, or image files from appearing in the SERP.
How Crawlers Interact with Robots.txt
When crawlers visit your site, the first thing they look for is a robots.txt file. This file tells the crawler which content to crawl and index and which content should be avoided. Basically, it works by blocking the crawlers from certain content and redirecting it elsewhere.
Blocking URLs with Robots.txt
You may want certain urls to be blocked by robots.txt to keep Google from indexing private photos, expired special offers or other pages that you’re not ready for users to access. Using it to block a URL can help with SEO efforts.
Managing Duplicate Content
Although not the best option, robots.txt can also solve issues with duplicate content. When a robot begins crawling, it first checks to see if a robots.txt file is in place that would prevent it from viewing certain pages.
Google’s Directives for Robots.txt
Keep in mind that Google bots only acknowledge certain directives for a robots.txt disallow. As of late 2025, Google will ignore robots.txt crawl-delay, but it does support:
- User-agent: identifies which crawler the rules apply to
- Allow: tells crawlers which URL path can be crawled
- Disallow: identifies a URL path that cannot be crawled
- Sitemap: contains the complete URL of a sitemap
Risks of Incorrect Robots.txt Implementation
Is robots txt a vulnerability? It sure can be! If you install a robots.txt file incorrectly, you could inadvertently tell search engines to disallow all of your content. If this happens, your site will be removed from search engine results pages, having a negative effect on your traffic, conversions, and overall revenue.
Last but not least, try not to use robots txt disallow CSS or JavaScript files. Doing so could keep bots from properly crawling and understanding content, subsequently hurting your SEO.
Limitations of Robots.txt
It’s also worth noting that not all crawlers will obey your command. While Googlebot and other top-name crawlers almost always will, other, lesser-known crawlers may not. If there is something on your site that you absolutely do not want to be exposed to, it’s better to put it behind a password-protected file or paywall rather than a robots.txt file.
Expert Opinion on Robots.txt Disallow Strategies
Robots.txt helps control what search engines can and cannot crawl on your site, which is key for SEO. You might block pages with sensitive information or similar content to avoid keyword cannibalization. Knowing how to use it ensures search engines will focus on your content that matters the most.
Robots.txt files essentially tell crawlers they are not allowed to crawl a page. This is particularly important when optimizing your crawl budget, a key reason to utilize this tool for SEO. While Google and other crawl bots need to be able to crawl certain pages, not all content is relevant or needs to be indexed.
For instance, some pages might contain sensitive or private information you don’t want to index, or entire segments of the website are irrelevant to organic search campaigns.
In any case, knowing how to utilize your robots.txt is helpful in ensuring search engine crawlers only see the content you want them to see.
Keep in mind, though, that this doesn’t make your content invisible. Crawlers might not be able to see it, but other people can. You’ll still need to set up the appropriate privacy parameters for confidential information.

Examples of How to Block URLs in Robots.txt
Here are a few examples of how to use block robots.txt:
Block All The Irrelevant Stuff
Maintain your crawl budget by blocking irrelevant pages, like old promotions, staging sites, admin areas, shopping cart pages, or internal search results pages. This will keep your main content wide open for crawlers. You can add the following line in your robots.txt file:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
Block a Specific URL
If you want to block a specific page or directory, you can do so by adding this line in your robots.txt file.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private.html
If you want to block several URLs:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private.html
Disallow: /special-offers.html
Disallow: /expired-offers.html
Block a Specific File Type
If you want to block a specific file type from being indexed, you can add this line to your robots.txt file:
User-agent: *Disallow: /*.html
Using a Canonical Tag
If you want to prevent search engine robots from indexing duplicate content, you can add the following canonical tag to the duplicate page.
rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com/original-url”

It’s important to note that canonical tags and robots.txt files work complementarily but handle different aspects of SEO. Canonical tags are HTML elements that signal which version of duplicate or similar content should be indexed, while robots.txt operates at the server level to control crawler access to pages.
While robots.txt can block crawling, it doesn’t prevent indexing if pages are linked externally, making canonical tags necessary for properly consolidating duplicate content signals. Using both tools strategically (robots.txt for crawler efficiency and canonicals for managing duplicate content) creates a more comprehensive approach to managing how search engines interact with your site.
Keeping Important Resources Crawlable
Now, you don’t want to disallow all resource files with robots.txt, just the ones you don’t need. As such, you must be very specific about the blocked internal resources in robots.txt, taking care not to block critical elements that hinder functionality, like JavaScript, CSS, and image files.
Use robots.txt disallow everything directory blocks for specific paths with non-essential content, and exclude critical elements in the process.
Handling Resource Files and Crawl Budget Optimization
As mentioned, you need to ensure search engine bots can access the files on your website that maintain functionality. If you disallow all resource files with robots.txt, crawlers won’t be able to understand your website’s content and what it’s all about, including:
- Images with Schema markup that complement text content
- JavaScript or CSS language that might include other structured data
To maximize your robots.txt usage, you should:
- Use robots.txt disallow strategically to conserve crawl budget.
- Combine with XML sitemaps for optimal indexing.
Doing this will ensure that crawlers can comb your most critical pages while blocking ones that might waste the crawl budget, allowing for faster and better indexing.
Remember that a robots.txt disallow directive only prevents search engine crawlers from accessing specific pages. It doesn’t guarantee those pages won’t appear in search results if they’re linked from other websites, which is why sensitive content should be protected using noindex meta tags or HTTP headers. For truly private content that shouldn’t appear in search results, implementing noindex tags is essential since they explicitly tell search engines not to include those pages in their index, regardless of how they discover the URLs
Getting Started With Robots.txt
Before you start putting together the file, check to see if you already have one in place.
To find it, just add “/robots.txt” to the end of any domain name—www.examplesite.com/robots.txt. If you have one, you’ll see a file that contains a list of instructions. Otherwise, you’ll see a blank page.
Next, Check if Any Important Files Are Being Blocked
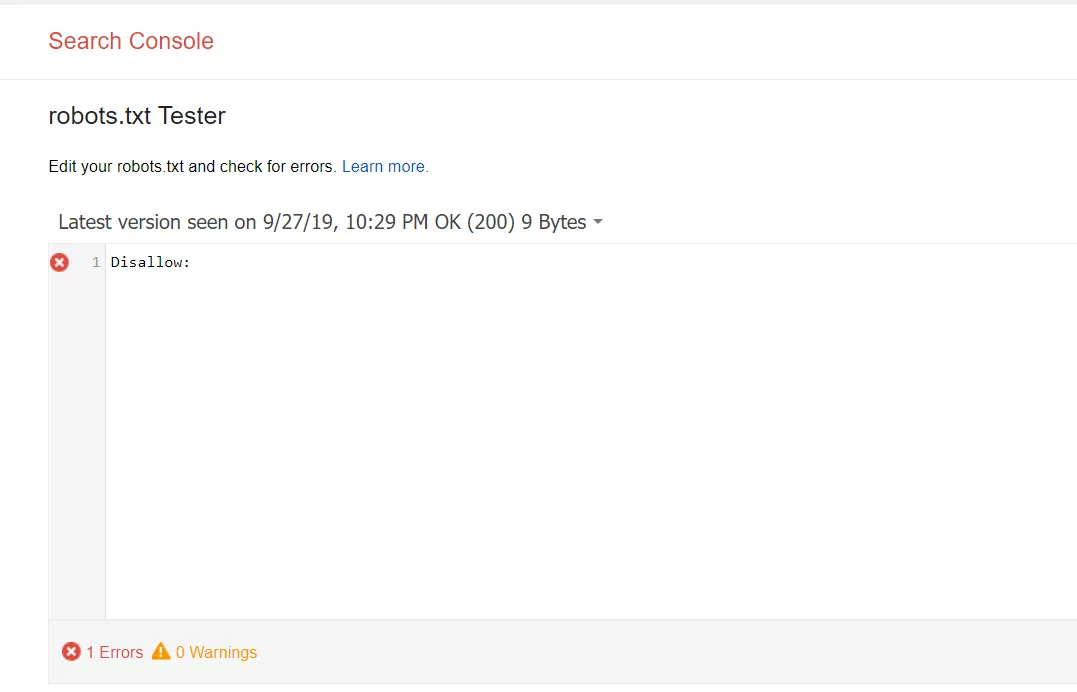
Head over to your Google Search Console to to check whether your file is blocking any important content. The robots.txt Tester will reveal whether your file is preventing Google’s crawlers from reaching certain parts of your website.
It’s also worth noting that you might not need a robots.txt file at all. If you have a relatively simple website and don’t need to block off specific pages for testing or to protect sensitive information, you’re fine without one. And—the tutorial stops here.
Setting Up Your Robots.Txt File
These files can be used in a variety of ways. However, their main benefit is that marketers can allow or disallow several pages at a time without having to access the code of each page manually.
Here are a few robots.txt file examples that will result in one of the following outcomes:
- Full allow—all content can be crawled
- Full disallow—no content can be crawled. This means that you’re fully blocking Google’s crawlers from reaching any part of your website.
- Conditional allow—The rules outlined in the file determine which content is open for crawling and which is blocked. If you’re wondering how to disallow a url without blocking crawlers off from the whole site, this is it.
If you would like to set up a file, the process is actually quite simple and involves two elements:
- The “user-agent,” which is the robot the following URL block applies to
- “Disallow,” which is the URL you want to block.
These two lines are seen as one single entry in the file, meaning that you can have several entries in one file.
Formatting Your Robots.Txt File
Once you’ve determined which URLs you want to include in your robots.txt file, you’ll need to format it correctly.

When setting up your file, you should add the following components:
User-Agent
This is the robot that you want the following rules to apply to. It’s often written in the following format:
User-agent: [robot name]
The most common robots you’ll find here are Googlebot and Bingbot
Disallow
This is the part of the file where you’ll specify which URLs should be blocked. The syntax for this usually looks like:
Disallow: [URL or directory]
So, if you want to block the directory “/privacy-policy/”, you’ll want to add “/privacy-policy/” as your disallow entry.
You can also use wildcards in your robots.txt file, letting you block multiple URLs in one go.
Sitemap
The sitemap element is optional. However, search engines may take it as a sign that you’re trying to make sure your site is easily navigable and trustworthy. This can help your ranking in the SERPs.
Your sitemap entry should look something like this:
Sitemap: https://www.example.com/sitemap.xml
Once you have your file set up, all you have to do is save it as “robots.txt,” upload it to the root domain, and you’re done.
Your file will now be visible at https://[yoursite.com]/robots.txt.
Location
You should always place the robots.txt file in the root domain of your website.
Note that the address is case-sensitive, so you should not use capital letters. It should always start with an “/.”
How to Block URLs in Robots.txt
For the user-agent line, you can list a specific bot (such as Googlebot) or can apply the URL txt block to all bots by using an asterisk. The following is an example of a user-agent blocking all bots.
User-agent: *
The second line in the entry, disallow, lists the specific pages you want to block. To block the entire site, use a forward slash. For all other entries, use a forward slash first and then list the page, directory, image, or file type
Disallow: / blocks the entire site.
Disallow: /bad-directory/ blocks both the directory and all of its contents.
Disallow: /secret.html blocks a page.
After making your user-agent and disallow selections, one of your entries may look like this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /bad-directory/
View other example entries from Google Search Console.
How to Save Your File
- Save your file by copying it into a text file or notepad and saving as “robots.txt”.
- Be sure to save the file to the highest-level directory of your site and ensure that it is in the root domain with a name exactly matching “robots.txt”.
- Add your file to the top-level directory of your website’s code for simple crawling and indexing.
- Make sure that your code follows the correct structure: User-agent → Disallow → Allow → Host → Sitemap. This allows search engines to access pages in the correct order.
- Make all URLs you want to “Allow:” or “Disallow:” are placed on their own line. If several URLs appear on a single line, crawlers will have difficulties separating them and you may run into trouble.
- Always use lowercase it to save your file, as file names are case-sensitive and don’t include special characters.
- Create separate files for different subdomains. For example, “example.com” and “blog.example.com” each have individual files with their own set of directives.
- If you must leave comments, start a new line and preface the comment with the # character. The # lets crawlers know not to include that information in their directive.

Where Should I Upload My Robots.txt File?
Once you’ve downloaded and edited your Robots.txt file, it’s time to upload it to the root of your domain. Uploading your file depends on your platform or hosting site.
Some services, such as Blogger or Wix, won’t let you access the file directly. If this is the case, explore your platform’s settings to see what options are available to you.
If you can edit your robots.txt file directly, you’ll want to save it with UTF-8 encoding after you’re finished editing.
Now it’s time to upload your robots.txt file to the root of your domain. Since this part is so dependent on your domain hosting site, there is no one correct way to do this. Check with your hosting provider to see your next steps.

How to Test Your Results
Once you’ve saved your file, it’s time to test it. While Google Search Console offers a built-in testing tool for Googlebot, other search engines, such as Bing and Baidu, require different approaches or third-party tools for verification.
For comprehensive testing, SEO professionals often use Screaming Frog, where you can simulate different user agents and test robots.txt directives. Simply navigate to Configuration > Robots.txt > Settings, where you can input custom user-agents and test specific URLs against your robots.txt rules.
A critical aspect of testing is ensuring that essential resources remain accessible. Check that your robots.txt configuration doesn’t accidentally block JavaScript, CSS, or image files that are necessary for proper page rendering and Core Web Vitals performance.
This is particularly important for rich snippets and structured data implementation, as search engines need access to these resources to properly understand and display your enhanced search results.
Common troubleshooting scenarios to watch for include:
- 404 errors on robots.txt, which can occur if the file isn’t in the root directory
- Syntax errors, particularly with wildcards or incorrect formatting
- Unintentionally blocked URLs due to overly broad patterns
- Conflicting directives between different user agents
Best practice is to maintain a testing log and regularly audit your robots.txt configuration, especially after website updates or structural changes. If you discover issues, address them promptly to prevent potential impacts on your site’s crawlability and SEO performance.
How to Test Your Results in Google Search Console
Follow these steps to test your results in your Google Search Console account to make sure that the bots are crawling the parts of the site you want and blocking the URLs you don’t want searchers to see.
- First, open the tester tool and take a look over your file to scan for any warnings or errors.
- Then, enter the URL of a page on your website into the box found at the bottom of the page.
- Then, select the user-agent you’d like to simulate from the dropdown menu.
- Click TEST.
- The TEST button should read either ACCEPTED or BLOCKED, which will indicate whether the file is blocked by crawlers or not.
- Edit the file, if needed, and test again.
- Remember, any changes you make inside GSC’s tester tool will not be saved to your website (it’s a simulation).
- If you’d like to save your changes, copy the new code to your website.
Keep in mind that this will only test the Googlebot and other Google-related user-agents. That said, using the tester is huge when it comes to SEO. See, if you do decide to use the file, it’s imperative that you set it up correctly. If there are any errors in your code, the Googlebot might not index your page—or you might inadvertently block important pages from the SERPs.

Using Other Tools for Testing Robots.txt Disallow
In addition to Google Search Console, you can use many other tools to test your disallow and determine whether you’ve blocked internal resources in robots.txt the right way.
For example, you can use Screaming Frog and Ryte to do so, along with manual methods.
Using these tools, you can also manually check the results of robots.txt disallow by taking the following steps:
- Open a private browser window
- Directly access your robots.txt file in the URL bar (e.g. domain.com/robots.txt)
- If the file content shows up, you can paste specific URLs to test within Google Search Console or other tools and see which are “blocked” in accordance with the rules you have set.

Just be sure to keep robots.txt consistently updated to optimize SEO for long-term success, which will help you get and stay ahead of competitors without compromising indexing.
Modern SEO Practices: Crawl Budget Management
Alright, now that you know why robots.txt is important, let’s talk crawl budget! Think of it like your website’s VIP list—only the most important pages should get crawled. For big sites with tons of pages, you’ve got to make sure the search engine’s crawlers are hanging out in the right places. That’s where robots.txt comes in handy!
Why Crawl Budget Management Matters
With Crawl Budget Management, you don’t waste crawls on low-priority stuff: You wouldn’t want search engines spending time on your login pages, search results, or those random filtered product pages, right?
Spotlight on the VIPs: Use robots.txt to make sure your best content—like your product pages, blogs, and services—gets the attention it deserves.
Cut the clutter: Don’t let crawlers get lost in endless product filters or duplicate content (looking at you, printer-friendly pages).
Keep in mind that the crawl budget and SEO is always changing. For example, it used to be that Googleboty couldn’t render JavaScript-heavy pages. Now, it can block JS/CSS resources, which can affect crawl efficiency.
Best Practice Tip: Use Google Search Console to monitor crawl activity and identify sections where crawl budget could be better utilized. Screaming Frog and Ahrefs also offer tools to help monitor and analyze your crawl budget.
Robots.txt + JavaScript & SPAs: Let’s Get Technical
Don’t block JavaScript files: Search engines (especially Google) now need to see your JS files to understand and render your page. If you block them, it can prevent full rendering and understanding of your content.
Watch those dynamic URLs: For SPAs, robots.txt can help control which URLs and API endpoints are being crawled. But be careful not to block anything that’s crucial for rendering your content!
Pro Tip: Always test how Google sees your site using the URL Inspection in Google Search Console.
Robots.txt for Different Search Engines:
1. Bing
Similar to Google, but Bingbot loves a good sitemap. Be sure to include your sitemap link in robots.txt to help Bing find your pages faster.
While Google doesn’t support “crawl-delay” and certain other directives, Bing does via its crawler, Bingbot.
2. Yahoo
Slurp (Yahoo’s crawler) is basically retired. Yahoo now uses Bing for most search results, so no need to stress too much. But if you’ve got old Yahoo-specific directives, update those ASAP.
Because of its use of Bing, Yahoo also supports some of the directives that Googlebot doesn’t, including “crawl-delay.”
3. DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckBot is all about privacy. It respects your robots.txt rules, but unlike other search engines, it doesn’t track users. It also crawls much more slowly and less frequently. Make sure your site is privacy-first if you’re targeting DuckDuckGo users!
Pro Tip: If you’re optimizing for search engines beyond Google, make sure your robots.txt file is up to date for all the big players, not just one.
If you’re not sure how a particular search engine will respond to your robots.txt disallow, consider running a test using multiple search engine tools to gauge results. Depending on how each search engine interprets directives, you can figure out how to optimize for the engines your audience uses.
Avoiding Robots.txt Mistakes Like a Pro
We’ve all been there, robots.txt mistakes can mess up your SEO real fast. One wrong line, and you might accidentally block the entire internet from seeing your pages (yikes!). Here’s how to avoid the most common pitfalls.
Common Robots.txt Mistakes Include:
1. Blocking essential resources: If you accidentally block CSS or JavaScript files, crawlers can’t render your page properly. This is happening more and more by marketers who don’t understand how to use robots.txt. It’s like trying to read a book with half the pages missing.
2. Over-blocking: Be careful not to block entire sections of your site. For example, don’t disallow /category/ if that’s where your money pages live.
3. Bad syntax: One typo, and your robots.txt file can go rogue. Make sure to double-check every line!
4. Failing to update regularly: Frequent updates to your robots.txt file will help you avoid compromising your SEO and crawl budget, maintaining proper indexing and ranking. Conduct regular audits to gauge how search engines are interpreting your robots.txt disallow and optimize accordingly.
All of these mistakes can quickly affect your crawlability, indexing, and ranking. In a world where organic search traffic matters, that’s the last thing you want to do! Always be sure to check your robots.txt files and how they’re working to make sure you don’t accidentally make any of these costly mistakes.
Pro Tip: Use Google’s robots.txt Tester to preview how your site will be crawled and to catch any errors before they wreck your SEO.
Robots.txt FAQs
1. Where should I save my robots.txt?
Your robots.txt should be saved in the root domain of your website. The address should be lowercase and start with an “/.” For example, the file can be found at https://www.example.com/robots.txt but not at https://www.example.com/ROBOTS.TXT.
2. Should I always use wildcards in my disallow lines?
Using wild cards won’t be always necessary, and can actually cause problems if you’re not careful. When listing specific URLs, you should always list them completely, even if you think a wildcard might work.
3. Can I use robots.txt to block bots from a specific image?
Yes, you can. To block a specific image, you can use the “Disallow” command and specify the file type of the image (e.g., “Disallow: /*.png”).
4. Does my robots.txt need to be perfect for it to work?
While it’s essential to ensure your robots.txt is accurate, minor errors shouldn’t keep your file from working. You can use the tester tool in Google Search Console to test your file.
5. What if I want to block specific bots?
You can use the “User-agent” line to specify which bots to block. For example, if you want to block all bots except for Googlebot, you can use this:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
User-agent: Googlebot
Allow: /
6. What does disallow mean in a robot.txt?
Adding “disallow” to your robots.txt file will tell Google and other search engine crawlers that they are not allowed to access certain pages, files, or sections of your website, directing them to avoid that content. This will usually also result in your page not appearing on search engine results pages.
7. What does user agent * disallow mean?
Adding “user agent *” gives you the opportunity to disallow only some crawlers. For example, if you want Googlebot to still crawl your page but you don’t want Facebot (Facebook’s crawler) to do it, you would type “user-agent: Facebot”. This will block Facebot but still allow all other crawlers to index your page. If you want to block everyone, you would type “user-agent: *”. The star will block every crawler.
8. How can you block AI crawlers?
You might want to know how to disallow specific pages with Google robots.txt from AI crawlers, which is doable with the right steps.
You can do so by adding the AI crawler’s “user-agent” name to the disallow directive within your file. Each AI crawler has its own designated user agent to block.
9. What alternatives can I use to robots txt disallow?
Robots.txt should only be used to manage crawl access, not to control indexation. If you want to stop specific pages from appearing in search results, use other methods.
One option is the meta robots tag, which lets you prevent indexing of certain pages like login, checkout, or duplicate content. This tag also helps manage how dynamic pages such as product listings or blog posts appear in search.
Another effective method is password protection, which restricts access entirely. This ensures private pages and files stay secure, even if search engines ignore your robots.txt settings.
Fully Implement Robots.txt Disallow with Ignite Visibility
If you want to learn how to disallow all except for robots.txt on certain domains or pages, Ignite Visibility can assist with this and many other aspects of SEO. Our experts will be able to ensure only the pages and resources you want to index and rank will contribute to your strategy, helping you optimize your crawl budget and stay on top of the competition.
Specifically, with our help, you’ll be able to:
- Properly implement robots.txt disallow
- Avoid any errors that might appear with optimization
- Build a fully functioning and optimized website that dominates search results
- Supplement disallows with other SEO efforts in a comprehensive campaign
- And more!
Want to see what we can do for your rankings on Google and other search engines? Reach out to us today, and we’ll connect you with a member of our team to discuss your digital marketing needs.