If you want the pages on your website indexed quickly, then you need to understand the meaning of crawl budget for SEO.
It really effects all sites big and small. But often, large sites, sites with technically errors or sites with unique URL generating features really need to pay attention here.
But wait!
I’m getting ahead of myself. Let’s start a little slower.

Everything You Need to Know About a Crawl Budget for SEO
The concept of a crawl budget was once a bit of a guessing game among SEOs. However, thanks to a recent post by Google’s Gary Illyes, we’re all now much more informed.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about a crawl budget and offer some optimization tips.
What Is a Crawl Budget?
Before you can understand the concept of a crawl budget for SEO, you’ll first need to familiarize yourself with another term: Googlebot.
Googlebot is the name given to the automated agent that crawls around your site looking for pages to add to its index. You can think of it as a digital web surfer.
Since there are billions and billions of pages on the web, it would be impractical for the Googlebot to crawl them every second of every day. Doing so would consume valuable bandwidth online, resulting in slower performing websites.
So Google allocates a crawl budget for each website. That budget determines how often Googlebot crawls the site looking for pages to index.
Google defines the mission of the crawl budget as follows: “Prioritizing what to crawl, when, and how much resource the server hosting the website can allocate to crawling is more important for bigger websites, or those that auto-generate pages based on URL parameters, for example.”
Why is Crawl Budget Optimization Important for SEO?
The answer to this is fundamental and simple. The better a crawl budget is optimized to index a page the higher it will rank on Google.
It is crucial to make sure that if you have a large site, specifically eCommerce, or have added a lot of pages or have a lot of redirected pages that you have the crawl budget capacity to handle it.
This should not be a huge concern, however, as Google crawls indexed pages efficiently but it is certainly something to be aware of.
Crawl Rate Limit
The crawl rate limit is a bit different than the crawl budget. It defines how many simultaneous connections the Googlebot uses to crawl a site and the time it will wait before fetching another page.
Remember, Google is all about user experience. The reason that its bot uses a crawl rate limit is to prevent a site from being overrun by automated agents to such an extent that human users have trouble loading the site on their browsers.
Here are a couple of factors that affect the crawl rate:
- Website speed – If a site responds quickly to the Googlebot, then Google will increase the crawl limit rate. On the other hand, Google will lower the crawl rate for sluggish websites.
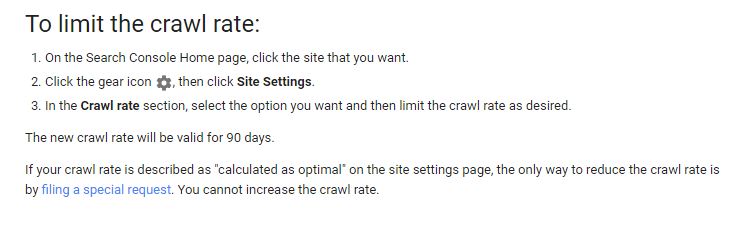
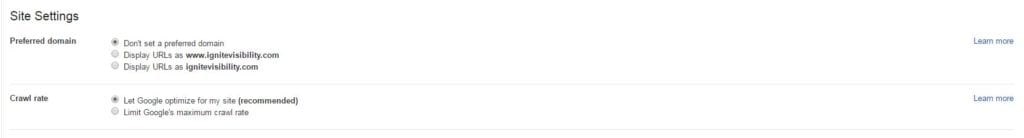
- Setting in Search Console – Webmasters can also set the crawl limit in Search Console. While they can’t increase the crawl rate, they can decrease it if they think that Google is doing too much crawling on their server.
Keep in mind that, while a healthy crawl rate might get pages indexed faster, a higher crawl rate isn’t a ranking factor.
Crawl Demand – Crawl Budget for SEO
Even if the crawl limit isn’t reached, Google might reduce the number of pages its bot crawls. The decreased activity from the bot is called a reduction in crawl demand.
What affects crawl demand? There are a couple of things:
- Popularity – Pages that are more popular (that is, they’re shared a lot on social media and receive links from other websites) tend to be crawled more often.
- Staleness – Google attempts to keep URLs from becoming stale in its index.
Also, site-wide events (such as a site move) might result in an increase in crawl demand. That’s because Google needs to reindex the content with the new URLs.
What Affects the Crawl Budget? – Crawl Budget for SEO
Basically, the crawl budget is a combination of the crawl rate and crawl demand. According to Illyes, the crawl budget is the number of URLs that the Googlebot can and wants to crawl.
Fortunately, Google has identified exactly which factors affect the crawl budget. Here’s a list of them, ranked in order of importance:
- URL parameters – It’s often the case that a base URL (for example, “https://mysite.com”) added with parameters (for example, “https://mysite.com?id=3”) returns exactly the same page. That kind of setup could result in numerous unique URLs counting towards the crawl budget even though all those URLs return the same page.
- Duplicate content – In some cases, URLs can be totally unique without request parameters and still return the same content. That will adversely affect the crawl budget as well.
- Soft error pages – Soft 404 error pages also impact the crawl budget. Fortunately, they’re also reported in the Search Console.
- Hacked pages – Sites that have been victimized by hackers can see their crawl budget limited.
- Infinite spaces – Sites that have unlimited links (such as calendars where users can click on a day, month, or year) will find that the Googlebot wastes its crawl budget on links that might be unimportant.
- Low-quality content – If the site suffers from poor quality, then it’s likely Google will limit the crawl budget.
How to Optimize Your Crawl Budget
Now that you’re familiar with the concept of a crawl budget for SEO, it’s time to optimize your site accordingly. Here are several ways to do just that.
1. Use Free Tools
– Both Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools provide you with plenty of information about problems that could be adversely affecting your crawl budget. Be sure to use them and configure them for all the sites you’re monitoring.
Then, check back with those tools from time to time to see if your sites are experiencing any problems. For example, if Search Console reports that one of your sites has some soft 404 errors, be sure to fix that problem immediately.
Remember, both Google and Microsoft want you to succeed online. That’s why they provide those tools free of charge.
2. Make Sure Your Pages Are Crawlable
– It’s tempting to take advantage of the wonders of modern technology to such an extent that you make it difficult for the Googlebot to crawl your site. Resist that temptation.
For example, technology like AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) loads content so that users don’t have to refresh the page. However, content loaded by AJAX might not be accessible by the Googlebot. This is a big topic that spams beyond SEO crawl budges, so we will save it for another post. But basically, you need to have an HTML base.
Also, use a sitemap and make sure that it’s always up to date. Fortunately, content management systems like WordPress make it easy to do that.
3. Limit Redirects
– Every time one of the pages on your site redirects to another page (with a 301 or 302 redirect), it uses a small part of your crawl budget. That means if you have a lot of redirects, your crawl budget could get depleted before the Googlebot crawls the page you want to be indexed.
4. Eliminate Broken Links
– If you have a lot of broken links on your site, you’ll need to get those cleaned up if you want to maximize your crawl budget.
Fortunately, it’s easy to find broken links with a tool like Screaming Frog. Also, be sure to check with Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools from time to time.
5. Avoid Using URL Parameters
– As we’ve seen, you can eat up a significant chunk of your crawl budget with different URL parameters that point back to the same page. You can eliminate that problem, of course, by eliminating URL parameters completely.
For example, if you’re running an ecommerce site, you might use the following URL to display a specific product: https://mysite.com/shop?productId=5. Instead, change that URL to https://mysite.com/shop/productId5 so something like that. In doing so, you’ll eliminate at least one request parameter.
If you must use request parameters, be sure to tell Google how to handle those parameters in the Search Console. Just click on “Crawl” in the left-hand sidebar and select “URL Parameters” from the menu that appears. On that page, you can edit your suggestions and add new parameters so that Google doesn’t index duplicate pages. This will change your crawl budget for SEO. But be really careful here, the wrong parameter can destroy your website.
6. Use Internal Linking
– It’s arguably the case that one of the most overlooked aspects of SEO today is internal linking. Keep in mind, though, that it’s typically best to link internally to your most profitable pages. That way, the Googlebot will see those pages more frequently.
7. Use External Linking
– A recent study shows that there’s a correlation between external links and the number of times the Googlebot crawls a site. That’s why it’s important to get external links pointing to your site.
It’s beyond the scope of this article to go into all the ways that you can build external links. View this comprehensive list of backlinking strategies for more info.
8. Improve Your Server Speed
– It’s important to do some pre-sales research before you select a hosting provider. That’s because you want a host that responds very quickly to server requests.
The faster that your server responds to a page request, the more pages that the Googlebot will crawl.
9. Cache Your Pages
– Speaking of speed, it’s a really great idea to cache your web pages. They’ll load faster not only for users, but also for the Googlebot, giving your site a boost in crawl rate limit.
Fortunately, it’s easy to cache pages on a WordPress platform with the W3 Total Cache plugin or the Super Cache plugin.
10. Optimize Page Load Speed
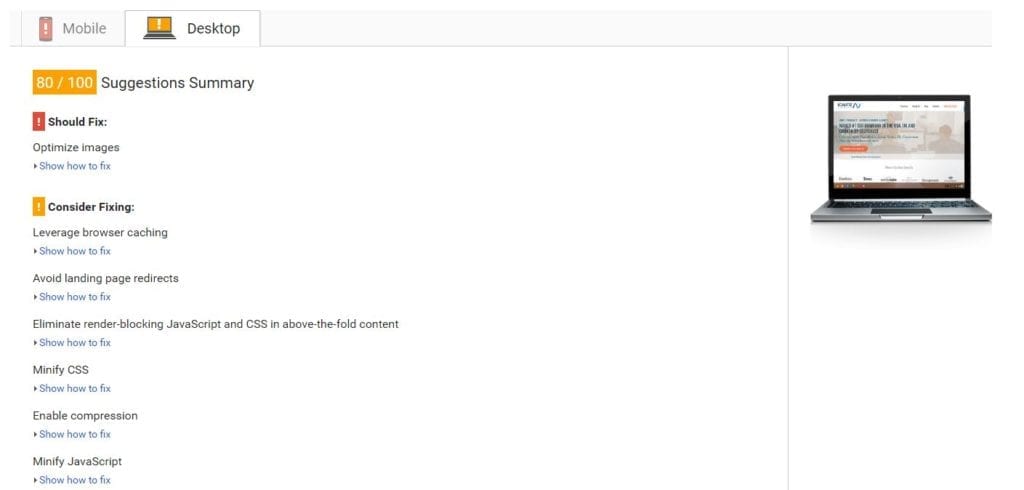
– Once you’ve put your site on a fast server and cached your pages, you still might not be done with speed optimization. Head on over to the PageSpeed Insights tool and see what Google thinks about your page speed.
You might find that there are still a few problems on your site that prevent your pages from loading as quickly as possible. For example, you might have render-blocking JavaScript or CSS on your pages.
Fortunately, Google not only tells you what’s wrong with your site, but also how to fix the problems that it’s identified.
Wrapping It Up Crawl Budget for SEO
Now you know a little bit more about crawl budgets, search engine optimization and how it affects your site.
Why not take some time today to put in place an action plan for optimizing your crawl budget? This can be really helpful for large websites and often leads to fixing many other problems outside of the crawl.