
Successful marketing is data-driven.
It relies on a constant stream of fresh, reliable data to guide its every decision. And no data is more relevant to your success than first-party audience data.
In this article, you’ll learn what first-party audience data is, how it’s collected, and why it is your key to successful marketing.
What is Audience Data?
Audience data is detailed information on how your target audience behaves online. It’s a combination of several sources coming together to form a complete picture.
Audience data includes information like:
- Hobbies and interests
- Demographics (age, location, etc.)
- Stage of the sales funnel
This information lets you create marketing campaigns tailored directly to your audience.
There are 4 types of audience data: first-party, second-party, third-party, and zero-party. Each of these types of audience data is collected in different ways and serves different purposes.
Before we go any further, let’s define each type and explain how they’re collected.
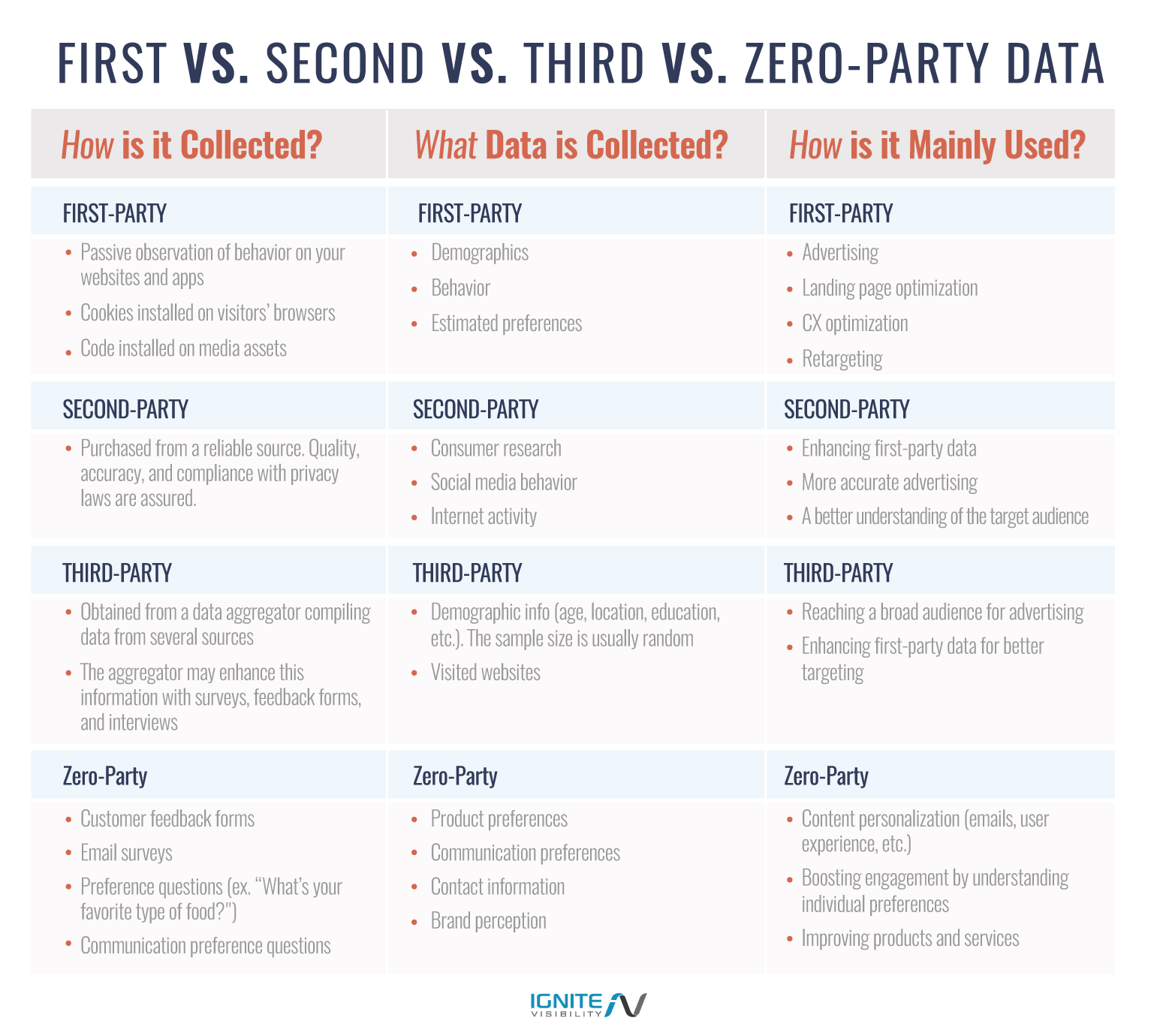
What is First-Party Data?
First-party audience data is the information you receive directly from your audience. It includes demographic information, audience behavior, and estimated preferences. Some examples include CRM data, subscription information, and behavioral data from your websites and apps.
It is collected through passive observation of behavior on your website, cookies installed on your visitors’ browsers, and code installed on media assets.
It is mainly used for advertising, landing page optimization, customer experience optimization, and retargeting. An estimated 87% of firms use first-party audience data as their primary source of information collection, making it the most popular of the 4 types of audience data.

First-Party Data Audiences
What is Second-Party Data?
Second-party data comes from a credible partner.
Since you work directly with the data collectors, you can trust that the data is accurate. Second-party data normally consists of things like consumer research, social media behavior, and internet activity.
Examples of second-party data include social media analytics and info bought from data marketplaces. It is often used in tandem with first-party audience data, to achieve more accurate advertising, and to help brands get a better understanding of their target audience.
When second-party data is combined with first-party audience data, it allows you to build ultra-accurate predictive models – especially if you deal with a smaller clientele.
What is Third-Party Data?
Third-party data comes from data aggregators.
It includes information such as demographic information and visited websites. Marketers use third-party audience data to help them reach a broader audience and narrow down their targeting efforts.
These aggregators don’t collect their data directly. Instead, they get it from other companies and compile it into a single report. They often get their information from customer surveys, feedback forms, and client interviews.
Most third-party data comes from advertising service demand-side platforms (DSPs). Certain marketplaces also sell third-party data, like Neilson and Acxiom.
Because they compile multiple datasets into a single report, the original demographics aren’t always clear. There’s also no guarantee aggregators collected it according to privacy regulations like GDPR.
That’s why third-party data is most effective when enhanced with first-party data. In fact, 46% of companies use both third-party and first-party audience data equally.
What is Zero-Party Data?
Zero-party data is information that customers intentionally and actively share with a brand.
It’s similar to first-party data, but the customer fully understands they’re sharing audience data. Compare this to first-party data collection methods like behavior data, where customers share info more passively.
Zero-party data is great because it requires no analysis. Your audience has provided you with the exact information you were looking for. This type of audience data includes things like customer feedback forms, email surveys, preference questions, and communication preference questions.
Examples of zero-party audience data include product preferences, communication preferences, communication information, and brand perception. It provides insight that can be used for content personalization, boosting engagement by understanding individual preferences, and improving products and services.
First Party Data vs. Second Party Data vs. Third Party Data vs. Zero Party Data
Evolution of Media Targeting Towards Privacy
In response to intrusive tracking by advertisers, we’ve seen a huge shift toward protecting user privacy. In a bid to protect consumers, companies like Google, Apple, and Amazon have made life increasingly difficult for marketers.
Many skeptics see this privacy shift as a disguised effort to restrict competition. But the bottom line is the same: your company needs to navigate these changes effectively.
Here are the biggest privacy-related issues marketers face this year:
The Demise of Third-Party Cookies
Modern advertising is hugely dependent on third-party cookies.
Marketers install them on users’ browsers to track their behavior after they leave their websites. That’s why you’ll see related ads following you around online after you’ve browsed for certain products or services.
For many, this represents a blatant violation of user privacy. Most consumers don’t understand what third-party cookies do, so they can’t fully consent to be tracked by them.
That’s why regulations, ad-blockers, and browser developers have increasingly restricted them.
Google plans to phase them out from Chrome in 2024, a move many see as the abolition of third-party cookies. Mozilla’s Firefox and Apple’s Safari have already done this.
This will change targeted advertising, but it won’t end it. Instead, targeting will shift to anonymized interest-based ad networks like Google’s FLoC.
First-party audience data will also become increasingly important. Zero and first party audience data requires consent, and therefore, isn’t seen as a violation of privacy.
Third-Party Data Restrictions
Some companies want to take user privacy further by banning all third-party tracking on their platforms.
The most notable example is Apple’s ban on third-party tracking without consent. App users must now explicitly agree to let companies track them, which only 20% do.
Third-Party Data Restrictions
As iPhones make up 53% of all American smartphones, this is a major blow to marketers wanting data on mobile users.
Marketers should expect policies like this to continue as consumers demand more privacy, especially the 23% of companies that are still dependent on third-party data.
Future of Data Usage in Marketing
As third-party sources face increasing restrictions, first and zero-party data hold increasing importance. Data-driven marketing isn’t going anywhere, but it’s changing.
Sketchy, unethical tactics will find a stage exit in the future’s marketing. Meanwhile, consent will play a lead role.
Consumers will generally always understand how companies are using their data. Companies will ask to track users explicitly or collect it in such a way that requires consent.
For instance, consumer surveys will become increasingly common. Companies will use products like Nicereply to make informed data collection easier for consumers.
Example of Customer Survey
3 Other Strategies to Collect Audience Data
Don’t worry. When it comes to collecting reliable and relevant audience data, all hope is not lost. Here are three other strategies that you can use.
Gather Conversion Data from Around the Web
Your Google Analytics conversation data should be one of the first places to look for audience data. You can learn a lot when you look at your demographic, technology, different channel, and Google Analytics benchmark reports to learn more about what type of customer is converting from your website the most.
Once you know who is resonating with your product the most, you can use this audience data to refine who you’re targeting with ads.
Platform Level Data
All of your social media platforms are going to give you some insight into your preferred audience and how they are consuming your content. If you post most of your content on Facebook, check out the Meta dashboard. Do you depend more on Instagram? Check out Instagram’s analytics.
Don’t forget to take a look at your followers, too. You can learn a lot about your audience by analyzing your followers and those who interact with your accounts the most.
A lot of website builders and hosts, like SquareSpace, also will provide you with platform-level data that you can use. If you’re a premium Google partner, they will give you access to geographic data, category data, and general information about your customer.
Google Trends & The Breakout Search Report
Google Trends is another great place to access quality audience data. Your Breakout Search Report, specifically, will show you all of the action around your top keywords. It’s also going to show you which keywords are going up and going down, which is great information to have for SEO purposes.
Why You Should Use Data-Driven Audience Personas
The best use of all of this audience data that you’re collecting is to create data-driven audience personas. These personas will help your entire company – from your paid ads department to your copywriting team – understand who it is that you want to target.
Since these personas derive from actual audience data, you can rest assured that your marketing team is targeting the correct audience – people that will buy your product or service and engage with your content. Because what is the point of creating incredible content if the wrong people are reading it?
First-Party Data FAQs
Next, we’ll answer the most common questions we receive about first-party data.
1. How Does First-Party Data Differ From Zero-Party Data?
Zero-party data is similar enough to first-party that some marketers consider it unnecessary. But there’s a crucial difference between the two: necessary consent.
First-party data collection occurs without the user being aware of it. Companies use session recording, device analytics, and other analytics to collect data passively.
There’s no third-party involved. But users don’t realize the site or app is recording their behavior.
However, zero-party data requires consent. Feedback forms, email surveys, and preference questions imply that the receiving company will use that data in some way.
2. Do Companies Sell First-Party Data?
Companies can sell first-party data following local privacy laws. However, companies that value customer privacy won’t and only use it for their services.
3. Is First-Party Data Collected From Outside Sources?
By definition, you can only collect first-party data from your sources (websites, apps, etc.). Data obtained from outside sources is second or third-party.
4. Can You Retarget With First-Party Data?
Yes, you can retarget visitors with first-party data. In fact, many companies often do this. You’ll notice that often after visiting a major brand’s website, you’ll see their ads following you around.
First-Party Data is the Future
While second and third-party data sources face increasing uncertainty, first-party remains unthreatened. By collecting your own data, you’re safe from privacy laws and shifts in consumer behavior such as using ad blockers and privacy browsers.
If your marketing relies on third-party data, act fast before tracking bans cripple your advertising efforts. First-party data is higher quality, more accurate, and privacy-compliant.
While moving away from third-party dependency takes effort, it’s an investment in your business’s future.
